Summary:
In this overview, we examine the ever-changing talent landscape, shaped by recent uncertainties. Businesses seek agile talent management amidst a competitive job market. HR teams, pivotal in growth planning, face the challenge of swift and informed talent decisions.
This case study explores key challenges and opportunities, with a focus on HrFlow.ai's enhancements for recruiters and candidates in an AI-powered talent marketplace.
Table of contents:
1. Overview
1.1 Abstract
2. History and Market Landscape of Talent Marketplace
2.1 Key drivers of the expanding Talent Marketplace market
2.2 Top leading Talent Marketplace solutions in the 2023 market
2.3 Talent Marketplace Businesses' Primary Revenue Stream
3. User Experience with Traditional Talent Marketplace
3.1. Analyzing the Recruiter's Experience
3.2. Analyzing the Candidate's Experience
4. Building an AI-Powered Talent Marketplace using HrFlow.ai
4.1 AI-powered Talent Marketplace for Recruiters
4.2. AI-powered Talent Marketplace for Candidates
5.How to Choose The Right Talent Marketplace
- Conclusion and Key Takeaways
1. Overview
1.1 Abstract
The last few years have seen a lot of change and uncertainty.
Businesses are inclined to create more agile talent management processes while delivering exceptional talent experiences.
HR teams these days have their plates full, taking on a growing number of tasks. They're not only helping companies plan for growth but also steering them through the ups and downs of a rocky economic ride and a cutthroat job market.
In this economic climate, quickly making the right talent decisions is more crucial than ever. Moreover, more people are entering and exiting the job market, and they've got fresh ideas about how, where, and the kind of treatment they expect from employers.
All of this means businesses need to rethink what truly drives productivity, engagement, and overall success.
This case study will put the talent landscape under the scope, to uncover where the biggest challenges lay - and opportunities.
2. History and Market Landscape of Talent Marketplace
2.1 The pre-pandemic talent landscape
Pre-pandemic, the talent marketplace was thriving in many ways. Job opportunities were abundant across various industries, and unemployment rates were relatively low in several regions.
Upsides:
- Abundance of Opportunities: Job openings were plentiful across diverse industries, contributing to a lower unemployment rate.
- Skill Development Emphasis: Companies focused on skill enhancement and upskilling initiatives to cater to specialized roles.
- Steady Economic Landscape: Generally stable economic conditions supported sustained job growth.
- Traditional Hiring Norms: Hiring processes largely followed conventional methods, relying on in-person interviews and local talent pools.
Downsides:
- Skill Gap Challenge: The mismatch between available skills and job requirements led to skill gaps in the market.
- Lengthy Hiring Processes: Recruitment procedures were often prolonged, lacking agility and efficiency.
- Impersonal Application Experience: Candidates encountered challenges in finding roles aligned with their skills, facing impersonal and time-consuming application processes.
2.2 The post-pandemic talent landscape
The post-pandemic talent landscape has witnessed a significant transformation as organizations grapple with establishing the "new normal" for work.
Upsides:
- Remote and hybrid work models, accelerated by the pandemic, have expanded the talent pool, driven by studies demonstrating that employees can maintain high productivity while working remotely.
- Simultaneously, there is a renewed focus on employee well-being and diversity, both pivotal for attracting and retaining talent.
- Certain businesses opted to expedite the launch of their talent marketplace in reaction to the pandemic.
Downsides:
- The World Economic Forum reports that 84% of employers are rapidly digitizing their working processes, creating an increased demand for digital skills. This digital shift has led to a pressing need for upskilling and reskilling, with 77% of CEOs, as reported by PwC, expressing concerns about the availability of key skills.
- A Microsoft survey reveals that over 40% of workers are contemplating leaving their jobs, underscoring the importance of fostering a more inclusive and supportive work environment.
2.3 Top leading Talent Marketplace solutions in the 2023 market
Here’s a list of some of the leading Talent Marketplace solutions in the Market:
- Beamery: Beamery is a leading talent engagement platform, utilizing AI to help businesses build talent pipelines and enhance employer branding. It focuses on nurturing potential talent through personalized engagement, revolutionizing the early stages of recruitment.
- Gloat: Gloat is an AI-driven career development platform, specializing in internal talent mobility solutions. It empowers organizations to identify and develop internal talent, promoting employee retention and engagement by aligning aspirations with opportunities.
- EightFold: Eightfold is a comprehensive talent intelligence platform, offering AI-driven solutions for talent acquisition, management, and upskilling. It aids in matching candidates to roles, predicting employee performance, and addressing skills gaps, covering the entire talent lifecycle.
- Fuel50: Fuel50 is a talent marketplace focusing on career pathing and employee development, offering personalized career experiences. It enhances employee engagement by providing clear career progression paths, addressing skills gaps, and fostering workforce agility within organizations.
2.4 Talent Marketplace Businesses' Primary Revenue Stream
Here's a list of billing business models for each of the mentioned companies based on payment types:
- Subscription-Based Models: monthly or annual subscription fees based on user count, features, or services.
- Enterprise-Level Pricing: Customized pricing structures for larger organizations to meet their specific requirements.
- Additional Fees: There is a possible extra fee for premium support, onboarding services, or advanced AI features.
- Consulting Services: There is a possible extra fee charge for consulting and implementation services to assist organizations in effectively using its platform.
- Renewal Fees: Enforces recurring subscription or license renewal fees for continued platform access.
- Licensing Fees: Charges licensing fees for the use of its talent intelligence platform, with pricing based on user count or specific services required.
- Implementation and Integration Services: Offers additional fees for customization, implementation, and integration services.
- AI Feature Upgrades: Provides different pricing tiers based on the level of AI-driven features and support.
- Customization Fees: Charges fees for customizing the platform to align with the organization's branding or specific needs.
- Success-Based Pricing: Considers a pricing structure based on the improvement in employee engagement or talent retention achieved through its platform.
3. User Experience with Traditional Talent Marketplace
User experiences with traditional talent marketplaces vary, with job seekers appreciating easy job search and resume submission but facing challenges in tailoring resumes for specific platforms.
3.1. Analyzing the Recruiter's Experience
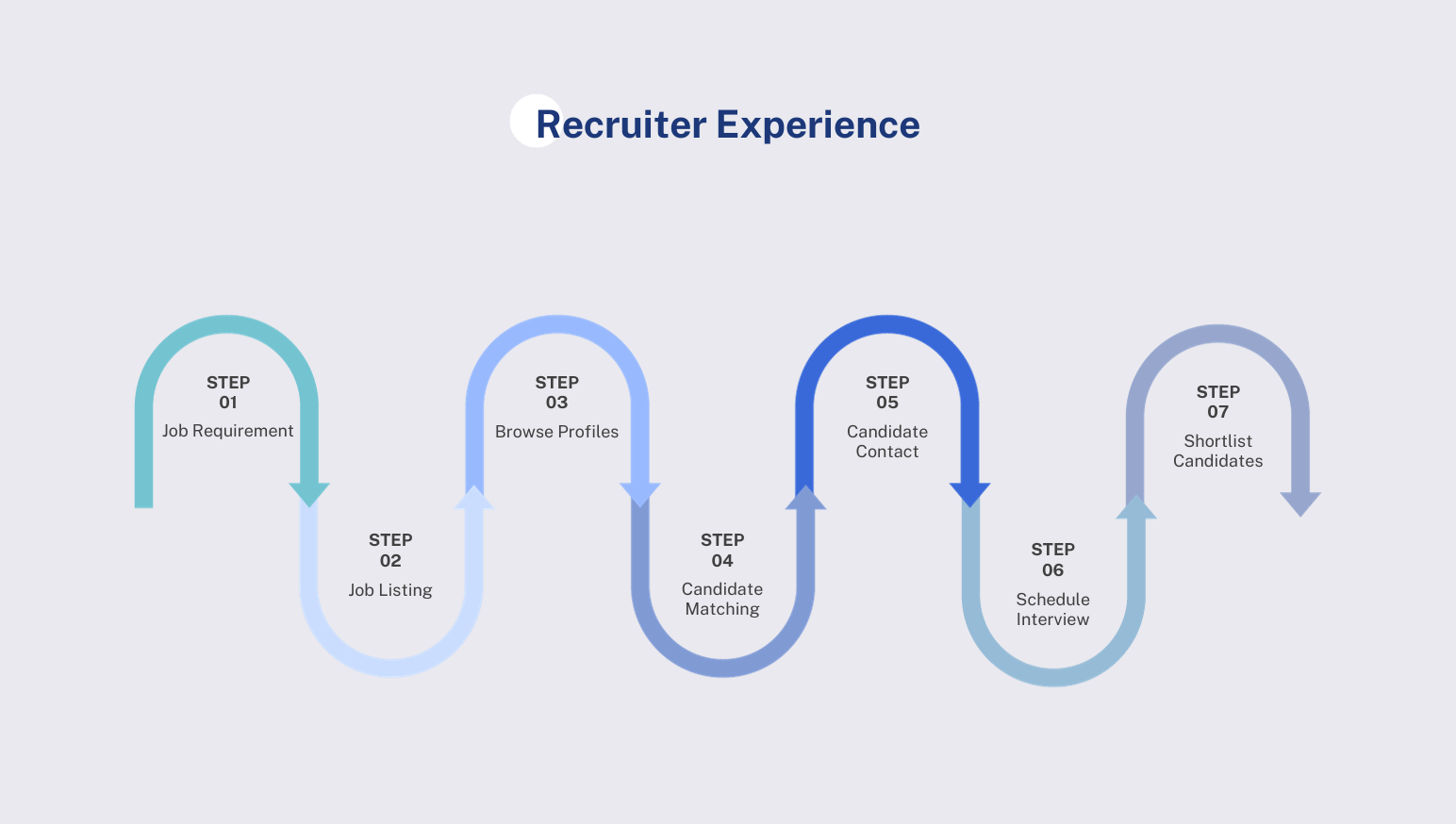
3.1.1 Job Requirement
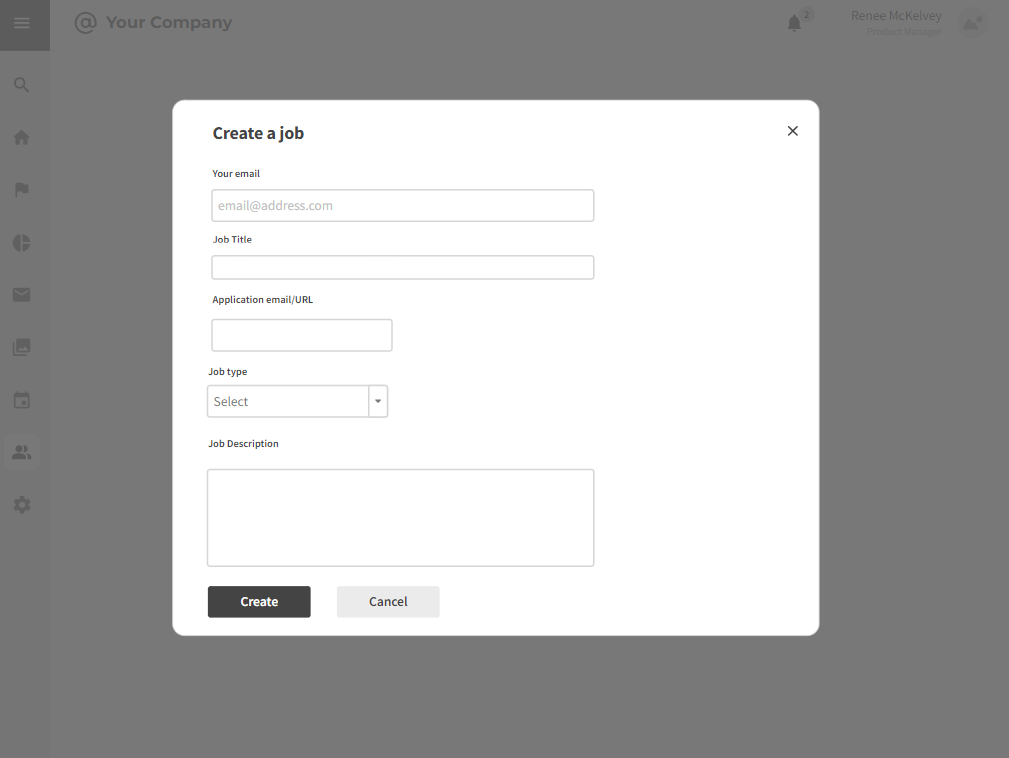
Strengths:
- Allows recruiters to define job requirements and postings
- Collaborative input from recruiters and hiring managers.
Weaknesses:
- Time-consuming and often manual process.
- Inflexible job templates that may not cater to all roles.
- Difficulty capturing nuances
Threats:
- Risk of failing to attract the right talent due to inadequate descriptions.
- Unclear requirements leading to unqualified applicants
Opportunities:
- Leverage AI to fill required fields automatically and create customizable posting creation
- Use of data analytics to refine job requirements and descriptions.
3.1.2 Job Listing
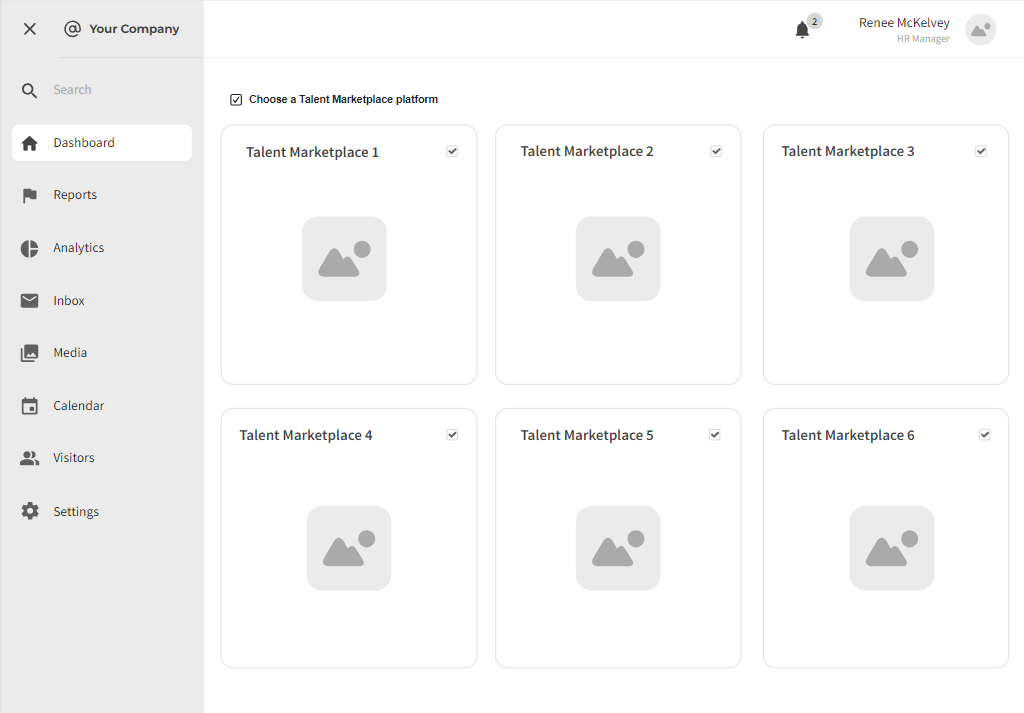
Strengths:
- Ability to post to multiple platforms.
- Potential for broad audience reach.
Weaknesses:
- Repetitive and often manual posting processes.
- Limited integration with social media and networks.
- No optimization of job advertisements.
Opportunities:
- Automated AI-powered job distribution.
- Integration with more platforms like social media.
- Optimization of job posts for maximum visibility.
Threats:
- Smaller applicant pool due to limited reach.
- Rapidly changing job board algorithms that may affect visibility.
3.1.3 Browse Profiles
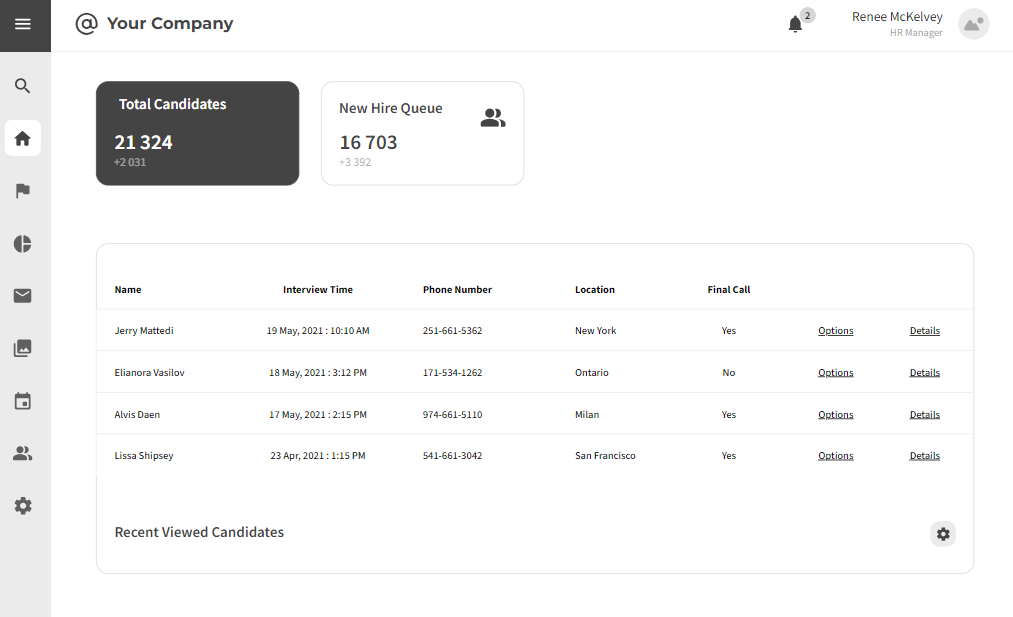
Strengths:
- Recruiters have access to detailed candidate profiles in one platform.
- Advanced filters and search functionalities streamline candidate discovery.
Weaknesses:
- Excessive data may lead to information overload, making it challenging to identify key candidate attributes.
- Platform may lack access to external sources for a more holistic candidate view.
Opportunities:
- Implement tools for easier interpretation of complex candidate data.
- Explore opportunities to integrate external data sources for a more complete candidate profile.
Threats:
- Risk of losing users to platforms with more advanced profile browsing capabilities.
- Increasing concerns about data privacy may impact the availability of certain candidate information.
3.1.4 Candidate Matching
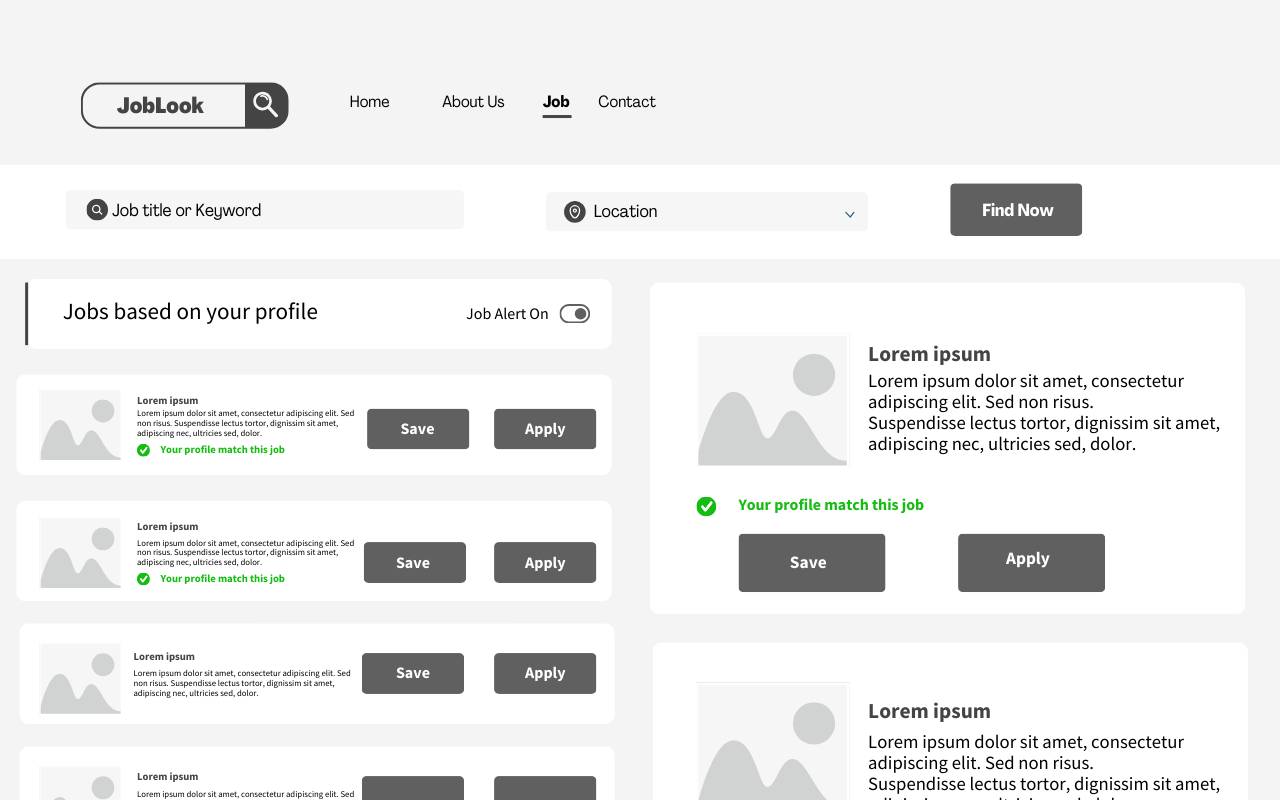
Strengths:
- Keyword search to filter candidates
- Matching algorithms, though basic
- Technical and personality tests
Weaknesses:
- Limited search capabilities.
- Simplistic or biased matching algorithms.
- Irrelevant applications.
- No evaluation of soft skills and culture fit.
Opportunities:
- Advanced semantic search capabilities.
- Relevant, nuanced, and unbiased matching algorithms.
- Automated screening tools assessing soft skills and culture fit.
Threats:
- Qualified candidates getting screened out.
- Time wasted on unqualified candidates.
3.1.5 Candidate Contact
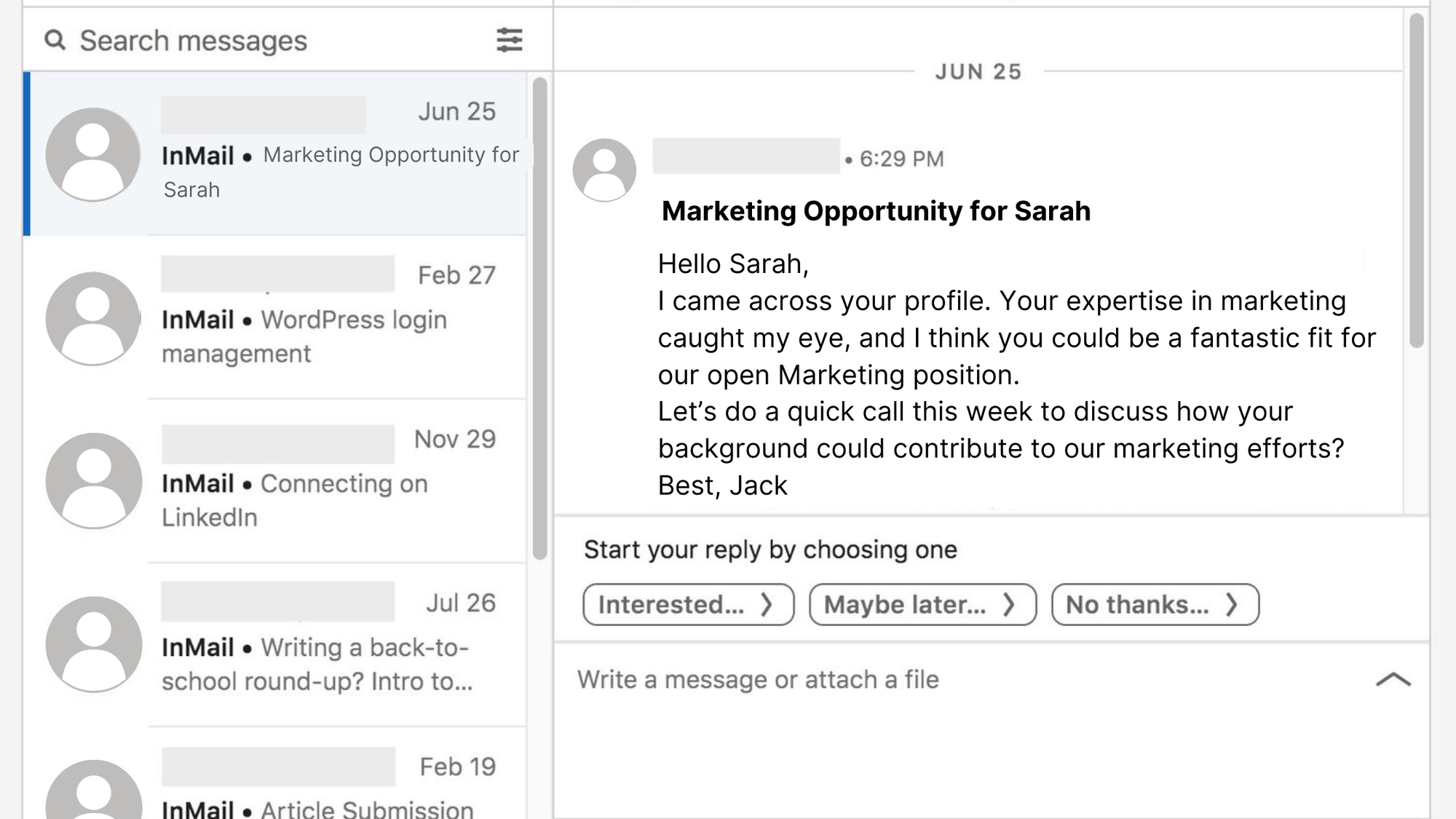
Strengths:
- HCM platform streamlines candidate contact in one interface.
- Automated reminders and notifications enhance communication efficiency.
Weaknesses:
- Potential for impersonal interactions, lacking a personal touch.
- Challenges in tailoring communication based on individual candidate preferences.
Opportunities:
- Implement features for more personalized candidate interactions.
- Opportunities to integrate with external communication platforms for a seamless experience.
Threats:
- Risk of losing users to platforms offering more advanced communication features.
- Concerns about data security may impact candidate trust in communication channels.
3.1.6 Schedule Interview
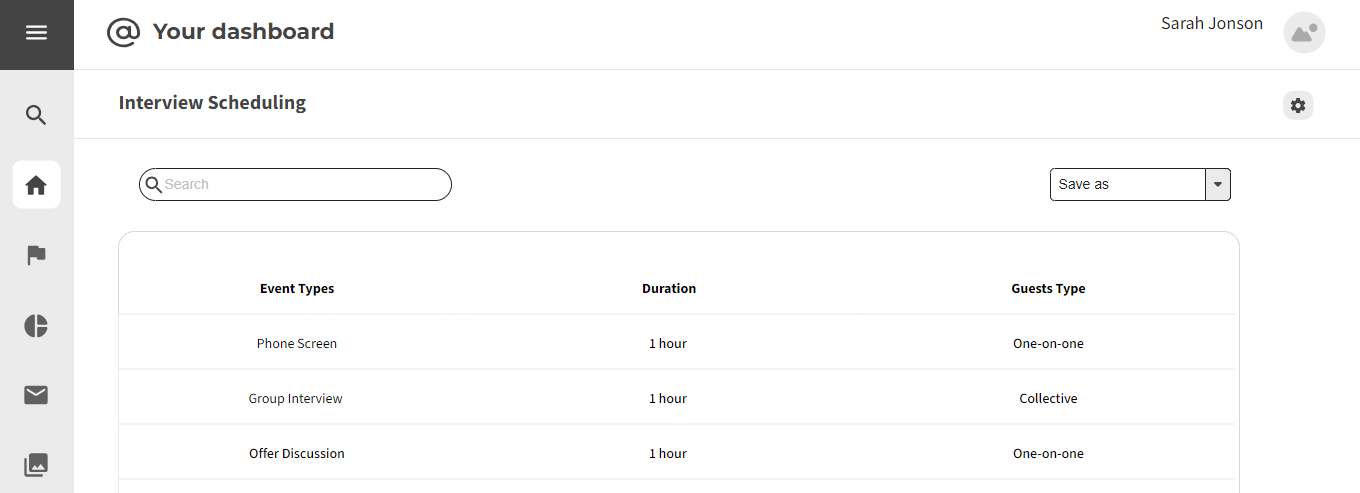
Strengths:
- Automated scheduling reduces delays and improves efficiency.
- Streamlined interactions among recruiters, candidates, and hiring teams.
Weaknesses:
- Automated scheduling may face challenges with varying availability.
- Excessive automated communication may lead to information overload.
Opportunities:
- Integrating AI for dynamic scheduling based on participant availability.
- Advancements in virtual interview tools for a seamless interview experience.
Threats:
- Technical issues during virtual interviews or automated scheduling may disrupt the process.
- Resistance to adopting new interview coordination methods may hinder successful implementation.
3.1.7 Shortlist Candidates
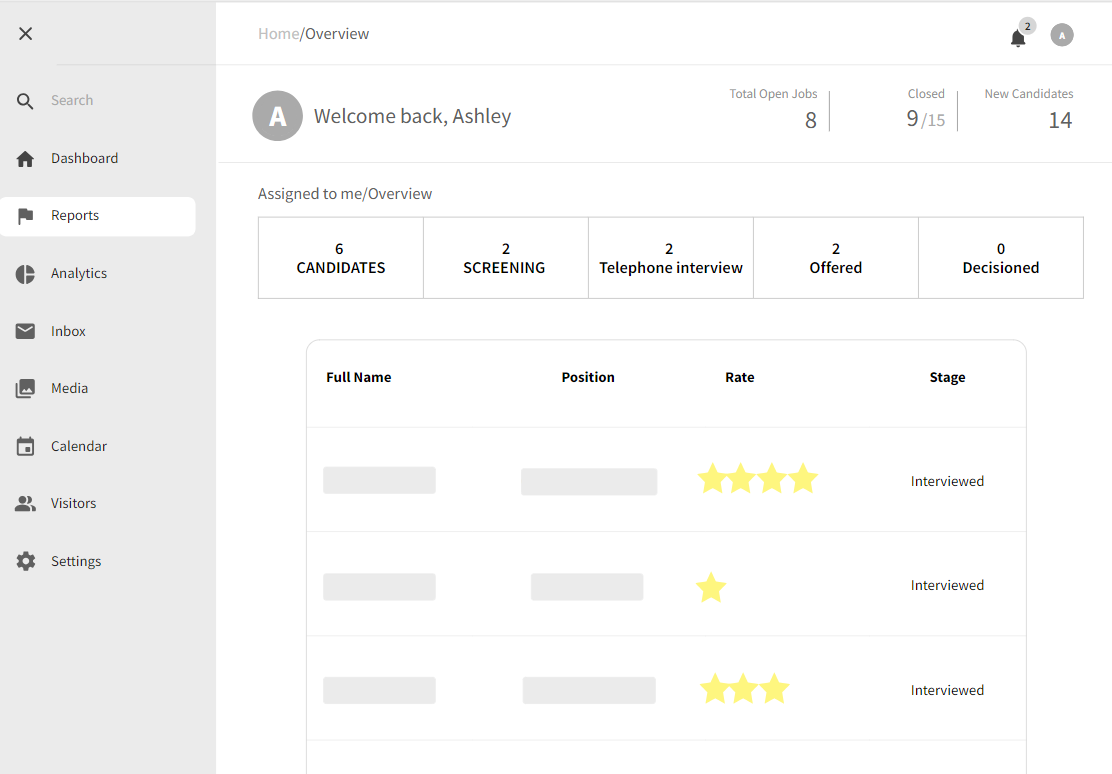
Strengths:
- Automated algorithms swiftly match candidates with job listings.
- Access candidates globally with varied skill sets.
- Analytics aid in informed shortlisting decisions.
Weaknesses:
- Risk of perpetuating biases in data affecting fair shortlisting.
- Some candidates may provide limited information.
Opportunities:
- Ongoing machine learning improvements for accuracy and fairness.
- Introduce interactive features and feedback mechanisms.
Threats:
- Risk of losing users to platforms with more advanced features.
- Data security and privacy issues may deter platform use.
3.2. Analyzing the Candidate's Experience
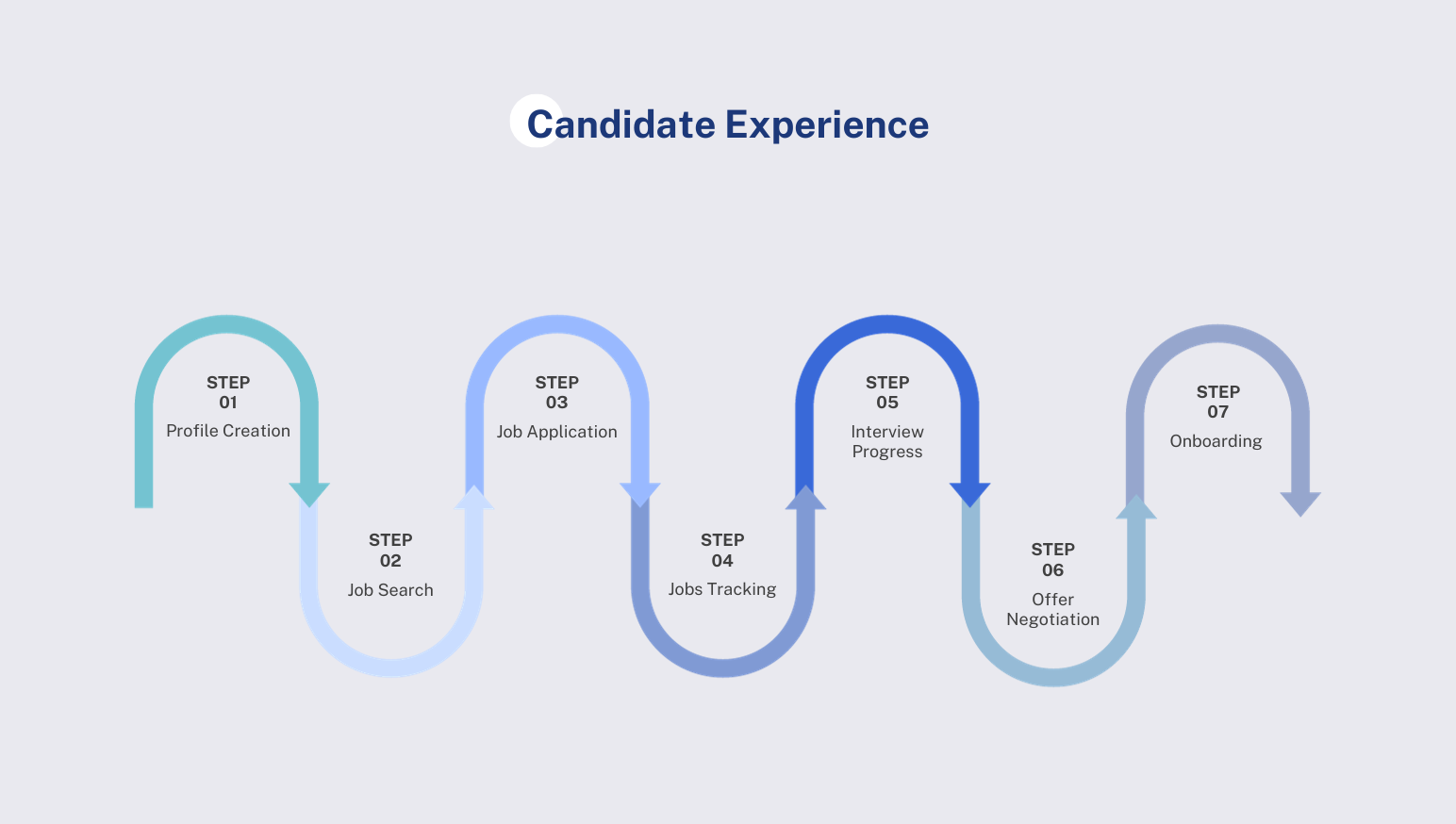
3.2.1 Profile Creation
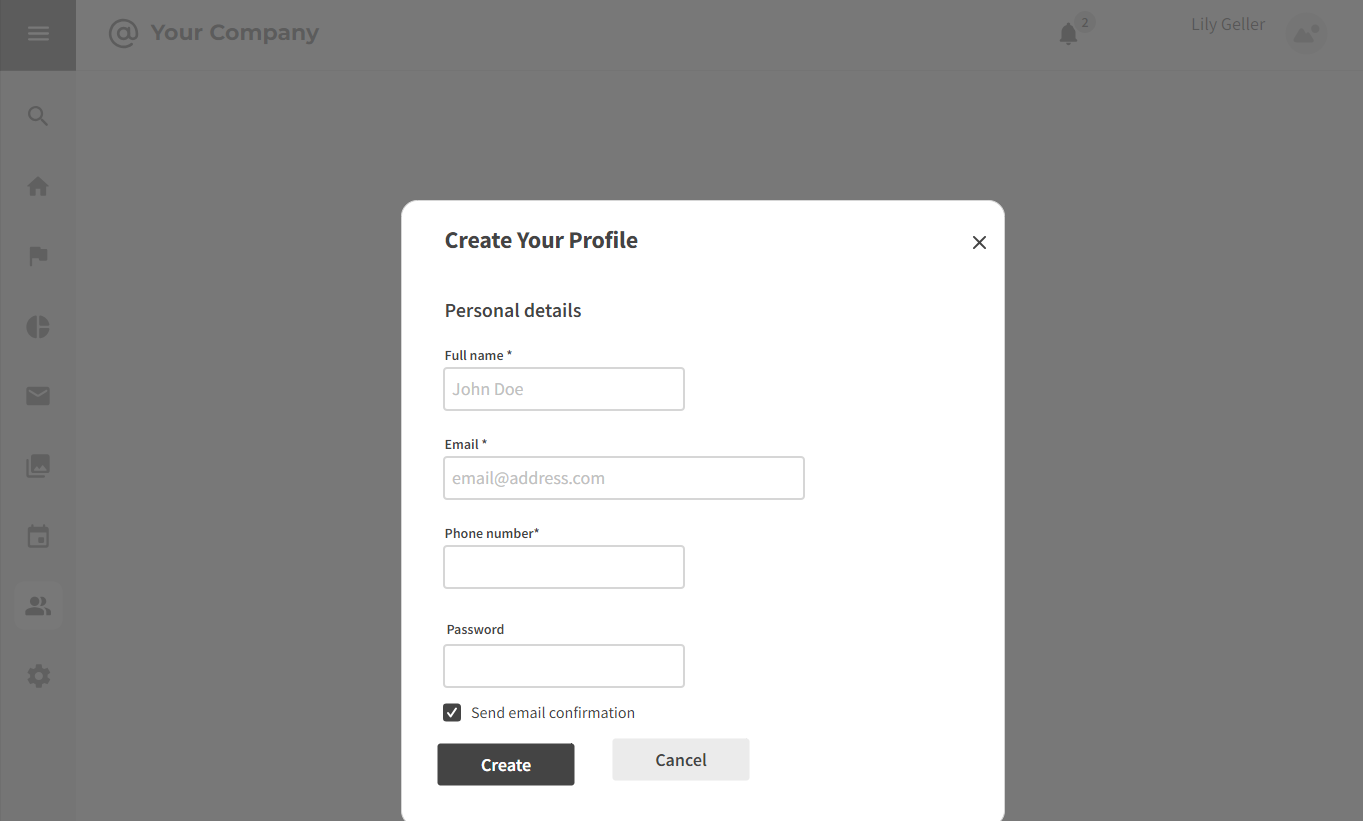
Strengths:
- Allows candidates to furnish detailed information, including skills, experience, and qualifications.
- Offers customization options enabling candidates to tailor profiles to specific job opportunities.
Weaknesses:
- Candidates may hesitate to provide extensive details due to concerns about the security of their personal information.
- Lengthy and complex processes may lead to candidate frustration and disengagement.
- Allowing information importation from professional networks might discourage candidates from investing time in manual profile creation.
Opportunities:
- Streamline profile creation by integrating AI tools to automate data input, enhancing efficiency for candidates.
- Optimize platforms for mobile devices, enabling candidates to create profiles on the go for enhanced user convenience.
Threads:
- Talent marketplaces with more advanced and user-friendly profile creation features pose a threat to adoption.
- Dissatisfied candidates sharing negative reviews can impact the reputation of the marketplace.
- Ineffective integration into job-matching algorithms may lead candidates to feel their detailed profiles don't improve job recommendations.
3.2.2 Job Search
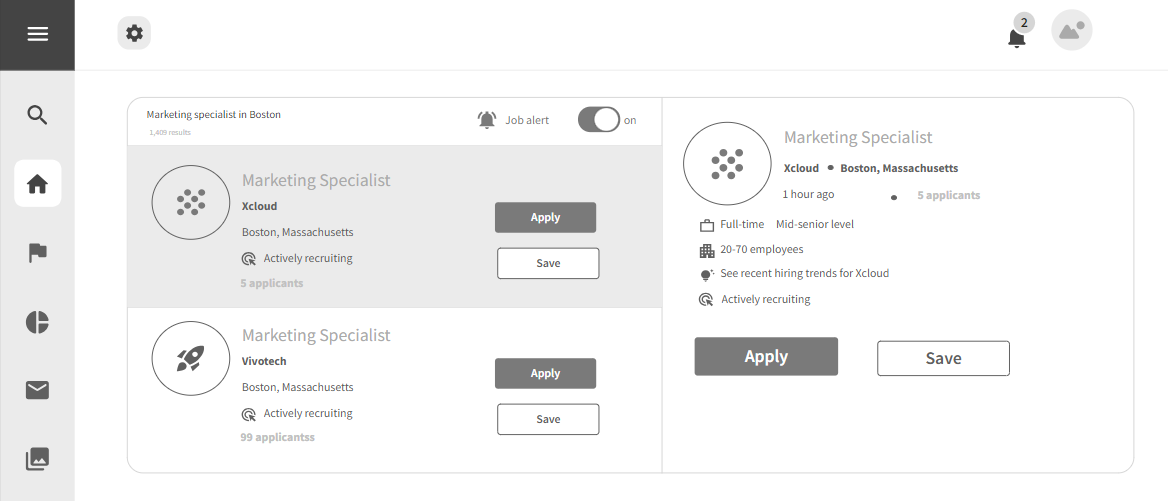
Strengths:
- Talent marketplaces offer a comprehensive range of job opportunities sourced from job boards, social media, and professional networks.
- Advanced search filters empower candidates to refine job results based on preferences, skills, and qualifications.
- Real-time updates on new job postings keep candidates informed about relevant opportunities.
Weaknesses:
- Limited Integration: Some platforms may have constrained integration with external job boards, limiting the visibility of available positions.
- Algorithmic Constraints: Job recommendations may be limited by algorithmic constraints, potentially leading to mismatches between candidates and suggested roles.
- Complex UI: A complex or unintuitive User Interface can pose challenges for candidates, affecting their ability to navigate and find suitable job listings.
Opportunities:
- AI-Driven Algorithms: Implementing AI-driven algorithms for job matching enhances recommendation accuracy, ensuring better alignment with candidates' skills.
- Expanded Integration: Increasing integration with a broader range of external job boards and platforms widens the pool of available job opportunities.
- Personalized Job Alerts: Offering personalized job alert features based on candidate preferences enhances proactive job discovery.
Threats:
- Poor User Experiences: Ineffective job matching or poor User Experiences may result in negative feedback, impacting the marketplace's reputation.
- Data Security Concerns: Concerns about the security of personal data during the job search process may discourage candidates from using the marketplace.
3.2.3 Job Application
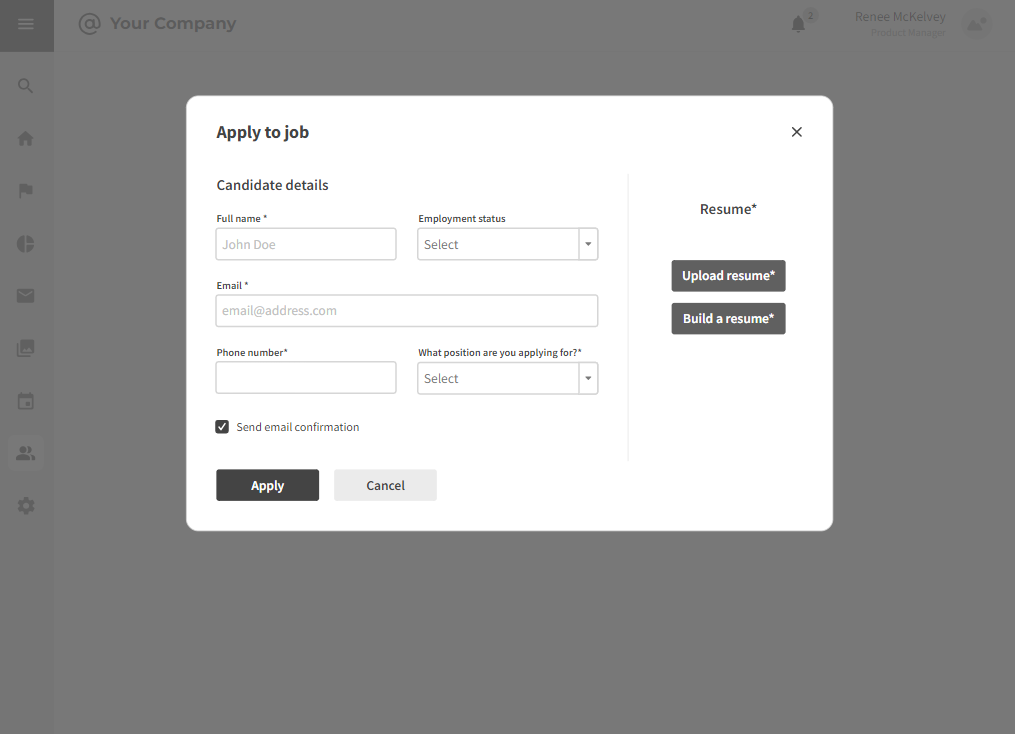
Strengths:
- Talent marketplace profiles offer a streamlined and user-friendly profile creation process, ensuring a positive candidate experience.
- Benefit from real-time updates on profile completion status, enhancing transparency and reducing uncertainty.
- Some platforms allow candidates to tailor their profiles, providing a personalized touch to showcase qualifications.
Weaknesses:
- Platforms with limited customization options may restrict candidates' ability to present their qualifications in a personalized manner.
- Technical problems or system glitches during profile creation can disrupt the candidate experience and lead to frustration.
- Constraints on document types or upload sizes may hinder candidates from providing comprehensive profile materials.
Opportunities:
- Automate aspects of the profile creation process with AI, making it more efficient and user-friendly.
- Allow candidates to customize their profile experience to impact engagement positively.
- Optimize the profile creation process for mobile devices, providing candidates with flexibility for on-the-go submissions.
Threats:
- The availability of other talent marketplaces with more advanced profile creation features may pose a threat to platform adoption.
- Poor profile creation experiences may lead to negative feedback, potentially impacting the reputation of the talent marketplace.
- Perceived or actual concerns regarding the security of submitted documents may deter candidates from using the platform.
3.2.4 Jobs Tracking
Strengths:
- Streamlined Process: Talent marketplaces offer a streamlined and user-friendly application submission process, ensuring a positive candidate experience.
- Real-time Updates: Candidates receive real-time updates on the status of their applications, enhancing transparency and reducing uncertainty.
- Personalization Options: Some platforms allow candidates to tailor their application profiles, providing a personalized touch to showcase qualifications.
Weaknesses:
- Inflexible Forms: Platforms with inflexible application forms may limit candidates' ability to present qualifications in a personalized manner.
- Frustrating Process: A frustrating application process with technical issues or system glitches can hinder the overall candidate experience.
- Document Constraints: Constraints on document types or upload sizes may hinder candidates from providing comprehensive application materials.
Opportunities:
- Implementing AI tools can automate aspects of the application process, making it more efficient and user-friendly.
- Introducing features that allow candidates to customize their application experience positively impacts engagement.
- Optimizing the application process for mobile devices provides candidates with flexibility for on-the-go submissions.
Threats:
- Competitive Features: Talent marketplaces with more advanced application features may pose a threat to platform adoption.
- Negative Feedback: Poor application experiences may lead to negative feedback, potentially impacting the marketplace's reputation.
- Security Concerns: Perceived or actual concerns regarding the security of submitted documents may deter candidates from using the marketplace.
3.2.5 Interview Progress
Strengths:
- Talent marketplaces streamline and coordinate various stages of the interview process, providing candidates with a centralized experience.
- Some platforms offer automated interview scheduling, reducing coordination efforts and enhancing convenience for candidates.
- The integration of feedback mechanisms within the platform allows candidates to receive timely and constructive feedback on their interviews.
Weaknesses:
- Platforms may offer limited options for interview formats, potentially restricting the variety of assessments candidates can undergo.
- Ineffective communication features may lead to misunderstandings or delays, impacting the overall interview experience for candidates.
- Technical issues during virtual interviews or assessments can create disruptions, causing frustration for candidates.
Opportunities:
- Implementing AI tools for interview assessments can provide more accurate evaluations of candidates' skills and compatibility.
- Introducing diverse interview formats allows candidates to showcase their abilities in various ways.
- Improving communication tools within the platform can foster clearer and more efficient interactions between candidates and recruiters.
Threats:
- Concerns about the security of interview-related data may lead candidates to choose alternative platforms.
3.2.6 Offer Negotiation
Strengths:
- Talent marketplaces streamline the offer creation and management process, reducing manual paperwork.
- Recruiters can easily track the status of offers, improving transparency in the hiring process.
Weaknesses:
- Some talent marketplace systems may have limitations in fully customizing offer letters to suit unique scenarios.
- Automated negotiation processes may lack the nuanced approach required for individual cases.
Opportunities:
- Integrating with e-signature tools can further expedite the offer acceptance process.
- Enhancements in customizable offer templates can cater to diverse roles and scenarios.
Threats:
- Ensuring that automated offer processes adhere to legal requirements and compliance standards is crucial.
- Automated processes may not adequately address individual concerns leading to offer declination.
3.2.7 Onboarding
Strengths:
- Talent marketplaces simplify onboarding processes, allowing candidates to complete paperwork and access materials efficiently.
Weaknesses:
- Overly complex onboarding modules may overwhelm candidates, potentially leading to delays and frustration.
- The inability to seamlessly integrate with other HR systems may hinder a cohesive onboarding experience for candidates.
- Lack of comprehensive training resources within the platform may hinder candidates' ability to familiarize themselves with onboarding processes.
Opportunities:
- Implementing AI tools for onboarding assistance can guide candidates through the process, providing support and clarifications.
- Optimizing onboarding processes for mobile devices enables candidates to complete tasks on the go, enhancing flexibility.
- Developing comprehensive training modules within the platform improves candidates' understanding of company processes and expectations.
Threats:
- Other talent marketplaces offering more advanced onboarding features may attract candidates away.
- Poor onboarding experiences may lead to negative feedback, impacting the marketplace's reputation.
- Concerns about the security of onboarding-related data may deter candidates from fully engaging in the onboarding process.
4.1. AI-powered Talent Marketplace for Recruiters
4.1.1 Job Requirement
- Recruiters can use HrFlow.ai Tagging API to pre-fill specific job offer fields.
- The Tagging API can adapt to dynamic job templates, offering recruiters more flexibility.
- HrFlow.ai Tagging API can also help you improve your job description SEO by providing relevant keywords and tags.
4.1.2 Job Listing
- Automated job listing to relevant channels: HrFlow.ai Talent Funnels allows Recruiters to post their job offers to multiple channels thanks to its impressive library of 200+ connectors.
- HrFlow.ai can also help create custom workflows that follow specific business logic set up by the client.
4.1.3 Browse Profiles
- HrFlow.ai Talent Funnels can help you easily connect to multiple talent pools of candidates.
- HrFlow.ai Recruiter Copilot offers recruiters advanced searching and scoring capabilities to source candidates efficiently.
- HrFlow.ai Searching & Scoring APIs can help you identify and target relevant prospects from various sources.
4.1.4 Candidate Matching
- HrFlow.ai Searching & Scoring APIs can help you identify and re-target relevant prospects from the past that could fit your current job openings.
- Text Parsing, Resume Parsing, and Tagging APIs can automatically update and enrich candidate contact information.
- HrFlow.ai's various connectors allow integration with communication platforms for streamlined candidate engagement.
4.1.5 Candidate Contact
- Recruiter Copilot can enhance the assessment process by providing more accurate evaluations of candidates' skills and compatibility.
- Profile Searching API allows recruiters to identify candidates with diverse skills and experiences, potentially leading to the implementation of more varied interview formats.
- Text tagging can contribute to a clearer understanding of a candidate's profile, improving communication between recruiters and candidates.
- Text Parsing helps to extract semantic entities from unstructured text and can enhance the overall assessment process by providing a more detailed understanding of candidates' experiences and skills.
4.1.6 Schedule Interview
- HrFlow.ai Usage Reports help recruiters review applicants' volume and sources. Moreover, HrFlow.ai offers structured and comprehensive data about applicants, which helps provide the best insights about your candidates.
4.1.7 Shortlist Candidates
- HrFlow.ai enhances candidate profiles with Recruiter Copilot, ensuring a more comprehensive view of candidates.
- HrFlow.ai's Searching and Scoring APIs can facilitate timely recruiter outreach by quickly matching candidates with suitable roles.
4.2. AI-powered Talent Marketplace for Candidates
4.2.1 Profile Creation
- Implement HrFlow.ai's Job Searching API for rapid and relevant job discovery, reducing the time spent on the sign-up process.
- Leverage HrFlow.ai's Job Searching API and Talent Copilot to optimize the sign-up process for candidates using mobile devices.
- Integrate Text Linking to automate data retrieval, allowing candidates to effortlessly populate information and streamline the sign-up process.
4.2.2 Jobs Search
- HrFlow.ai Talent Copilot employs AI to offer personalized talent recommendations, tailoring suggestions based on candidates' profiles and preferences, enhancing the talent search experience.
- Utilizing HrFlow.ai's Job Searching API, job seekers benefit from a refined job search that aligns with their interests and experience.
4.2.3 Job Application
- Resume Parsing and Tagging APIs can automatically fill in application fields, reducing manual entry for candidates.
- HrFlow.ai's various connectors enable a simplified job application process through seamless integrations with 200+ connectors.
- HrFlow.ai's Tracking API and Workflows can be configured to provide status updates and notifications about application progress.
4.2.4 Application Tracking
- The Job Parsing and Tagging API from HrFlow.ai automate application field completion, minimizing manual entry for candidates during the talent application process.
- HrFlow.ai's connectors simplify the application process by seamlessly integrating with 200+ connectors, facilitating the smooth submission of talent applications.
4.2.5 Interview Progress
- Talent Copilot helps candidates identify the most qualified job openings, indicating the incorporation of AI assessment tools for more accurate evaluations of candidates' skills and compatibility.
4.2.6 Offer Negotiation
- Talent Copilot helps candidates identify the most qualified job openings for them, indirectly contributing to a positive candidate journey in the offer negotiation stage.
4.2.6 Onboarding
- HrFlow.ai's onboarding support simplifies processes, enhances personalization, and ensures sustained engagement.
5.How to choose the right talent marketplace
Scalability:
- Choose a platform that scales across your entire organization for widespread impact.
- Look for vendors with experience deploying their solutions to thousands of employees.
Successful Implementations:
- Prioritize vendors with active customer communities and real-life success stories.
- Check for leaders at client brands sharing platform success on social media.
Core Functionality:
- Assess the core functionality of AI-powered platforms aligning supply and demand.
- Avoid technology masquerading as a talent marketplace; focus on purpose-built solutions.
Diverse Opportunities:
- Ensure the platform supports a range of opportunities beyond full-time roles.
- Opt for open integration to maximize access to projects, gigs, mentorships, and temporary roles.
Change Enablement and Implementation Support:
- Acknowledge talent marketplaces as a distinct technology category.
- Seek vendors offering customer support and change enablement for a smooth launch.
User-Friendly Design:
- Verify that the talent marketplace caters to users at all levels, not just recruiters.
- Prioritize intuitive design for seamless use by employees across the organization.
Efficient Onboarding:
- Choose platforms that can be implemented in weeks for swift and impactful results.
- Avoid vendors requiring extensive data collection or prolonged setup processes.
6.Conclusion and Key Takeaways
In conclusion, navigating the evolving talent landscape demands agile solutions. HrFlow.ai's AI-powered talent marketplace addresses challenges by enhancing the recruiter and candidate experience. Key takeaways include the importance of scalability, successful implementations, core functionality alignment, diverse opportunities, change enablement support, user-friendly design, and efficient onboarding for a competitive edge in today's dynamic economy. Embracing innovation in talent management is paramount to unlocking productivity, engagement, and overall success.

