Summary:
In a world of constant change, Human Capital Management (HCM) tools are rewriting the HR script. It's not just evolution; it's a reimagination of HR, where innovation reigns. This case study explores how HCM tools empower organizations, featuring trailblazers navigating this transformative journey.
Table of Contents:
1.Overview
1.1 Abstract
2.History and Market Landscape of HCM
2.1 The expanding opportunities in HCM market
2.2 Top leading HCM solutions in the 2023 market
2.3 HCM Businesses' primary revenue stream
3.User Experience with Traditional HCM
3.1. Analyzing the Recruiter's Experience
3.2. Analyzing the Candidate's Experience
4.Building an AI-Powered HCM using HrFlow.ai
4.1. Enhancing HCM for Recruiters: HrFlow.ai's Key Improvements
4.2. Enhancing HCM for Candidates: HrFlow.ai's Key Improvements
- How to Choose The Right HCM For You
6.Conclusion and Key Takeaways
1.Overview
1.1 Abstract
In a world where the boundaries of work and talent are constantly shifting, a silent revolution is taking place within the confines of Human Resources.
Human Capital Management (HCM) tools have emerged as the architects of change, redefining the way organizations perceive, harness, and elevate their most vital asset – their people.
This is not a story of evolution but one of reimagining the very essence of HR, where innovation and adaptability reign supreme.
The HCM narrative is no longer one of adherence to the norm but a journey toward empowerment, and this case study delves into the profound impact of HCM tools while shining a spotlight on the trailblazers charting this uncharted territory.
2.History and Market Landscape of HCM
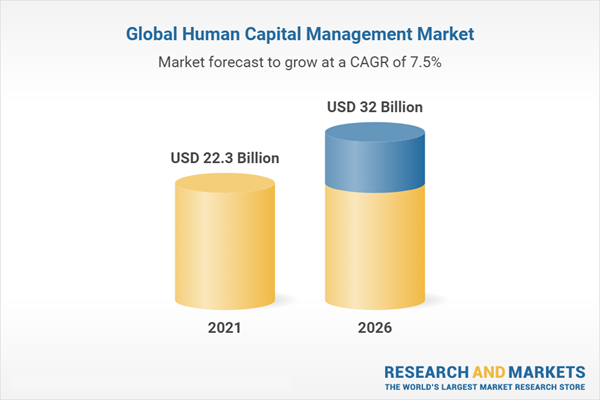
The global HCM market has experienced significant growth, with revenues exceeding $22.3 billion in 2021.
Industry experts predict that this growth will continue, projecting the market to surpass $32 billion by the end of 2026. This upward trajectory underscores organizations' increasing emphasis on effective talent acquisition and management.
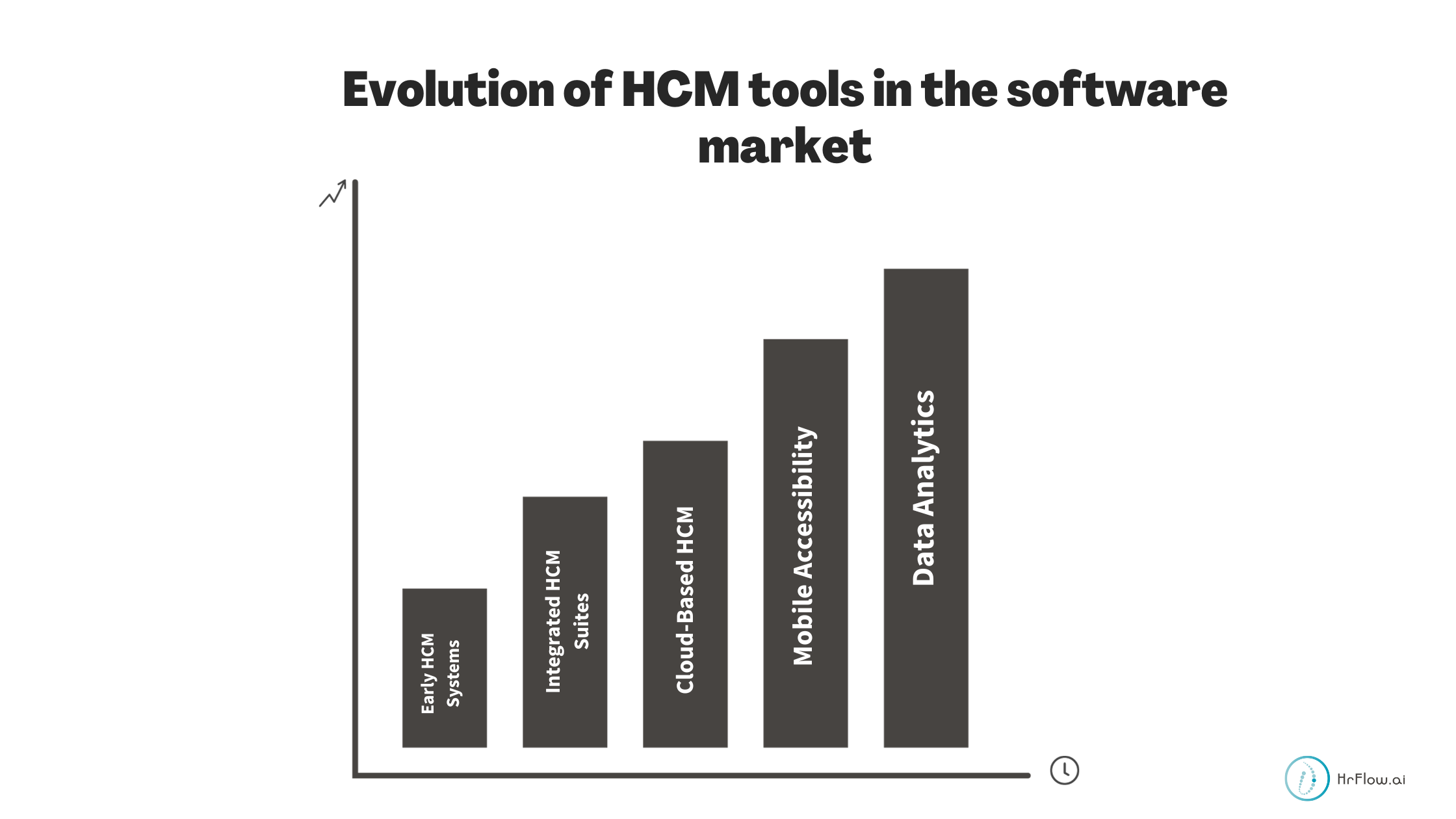
HCM tools have come a long way, their development can be summarized in the following stages:
- Early HCM Systems: Initially, HCM tools focused on basic HR functions, like payroll and employee records.
- Integrated HCM Suites: Over time, they expanded to include recruitment, talent management, and performance appraisal modules.
- Cloud-Based HCM: The shift to cloud-based solutions brought scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness to HR management.
- Mobile Accessibility: HCM systems adapted to the rise of remote work by offering mobile apps for on-the-go HR management.
- Data Analytics: The introduction of data analytics and AI-driven insights enabled better talent management and decision-making.
2.1 The expanding opportunities in HCM market
- Juggling a Diverse Workforce: Picture this—companies navigating the global business maze, wrestling with the task of handling a team as diverse as a buffet menu. Enter HCM software, the hero equipped to tackle the complexity of this environment and make workforce management a breeze.
- Boosting Employee Productivity: HCM solutions are like a secret weapon in a business's arsenal. They roll out the red carpet for employee excellence, offering talent management, performance tracking, and skill-development programs that turn your workforce into a productivity powerhouse.
- Dance with Regulations: Keeping up with rules and laws in the job world can be a real head-spinner. Thankfully, HCM software vendors swoop in with their bag of tricks, offering features that not only keep your data safe and sound but also make sure you're always playing by the rules.
- Security Tightrope: Now, let's talk about the elephant in the room—security. It's a tricky game for HCM vendors. Sure, cloud-based HR platforms promise growth galore, but they also bring their share of security headaches. Employers are now donning their detective hats, eyeing data privacy issues like never before. With the looming threat of HR infrastructure attacks causing chaos, it's a real make-or-break for business growth.
2.2 Top leading HCM solutions in the 2023 market
With billions invested in the HR Technology market - HR tech startups raised about $3.3 billion for 2023 according to Crunchbase - there are plenty of options for talent leaders.
- Workable: Offers cloud-based solution renowned for user-friendliness and a commitment to innovation. Workday has a 26.33% market share in the Human Capital Management category, and Workday has 35,469 customers in 10 countries.
- Workday HCM: Offers a cloud-based human resource management solution known for its comprehensive features, including core HR functions, talent management, and workforce planning.
- iCIMS Talent Cloud: Offers a cloud-based talent acquisition platform known for its robust features in recruiting and applicant tracking
- BambooHR: Offers a cloud-based human resource management solution celebrated for its robust features encompassing core HR tasks, talent management, and workforce planning.
2.3 HCM Businesses' primary revenue stream
Subscription fees constitute the primary revenue source for the HCM business. Below is an outline of the fundamental elements within its business model:
- Subscription-Based Model: Many HCM solution providers, such as Workday HCM, operate on this model. They enable their customers to pay a recurring fee to access their cloud-based HCM software. This fee covers regular updates, maintenance, and customer support.
- Tiered Pricing: Some HCM solutions like BambooHR offer different tiers of pricing based on the features and functionalities included. Customers can choose the tier that aligns with their specific needs and budget.
- Freemium Model: offering a basic version of their software for free, like Monday, with the option to upgrade to a premium version with more advanced features and capabilities.
- Per-User Pricing: Example: ADP Workforce Now charges customers based on the number of employees using the software. Organizations pay a fee for each user who accesses the platform.
- Custom Pricing: By offering custom pricing for larger enterprises with complex needs. Like Oracle HCM Cloud, the pricing is tailored to the specific requirements and scale of the organization.
3.User Experience with Traditional HCM
A KPMG report reveals that 2 out of 3 talent leaders are not happy with the outcomes of their current HR technology.
3.1. Analyzing the Recruiter's Experience
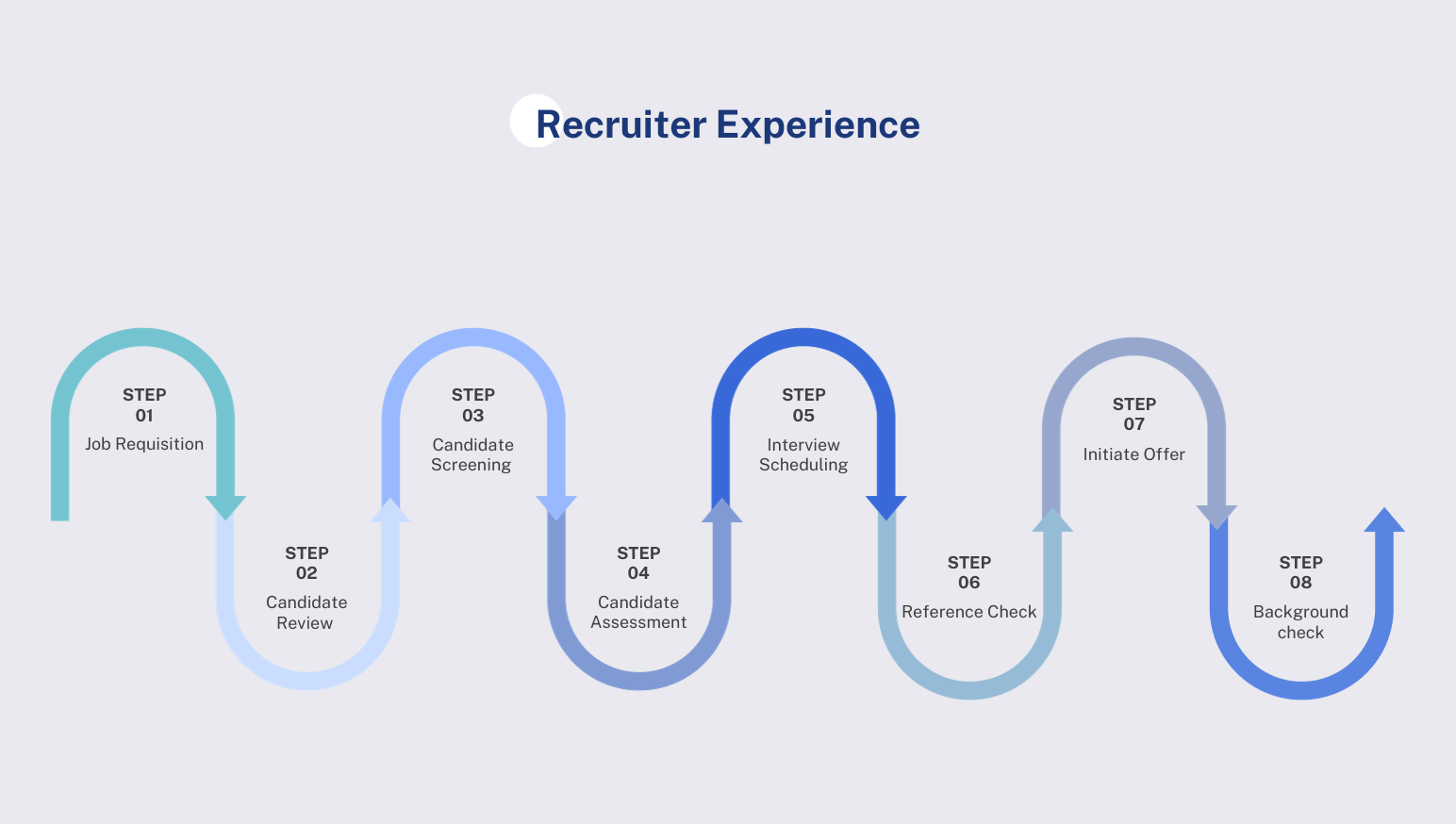
3.1.1 Job Requisition
Strengths:
- Efficiency: Automates job requisition creation, saving time.
- Standardization: Ensures consistency with templates, minimizing errors.
Weaknesses:
- Learning Curve: Training may be needed for advanced features.
- Dependency on Technology: Possible disruptions during system outages.
Opportunities:
- Integration Potential: Seamless connection with HR tools and external platforms.
- Customization: Ongoing improvements allow tailored requisition processes.
Threats:
- Security Concerns: Robust measures to address data security threats.
- Competitive Landscape: Vigilance in monitoring and adapting to evolving market trends.
3.1.2 Candidate Review
Strengths:
- Broad Reach: Integrates with various sourcing channels, expanding candidate reach.
- Automated Matching: Advanced algorithms enhance efficiency by matching candidates with job requirements.
Weaknesses:
- Limited External Reach: Some HCM solutions may have restrictions in accessing certain external job boards or niche platforms.
- Data Accuracy: Dependence on accurate data input for effective candidate matching can be challenging.
Opportunities:
- AI Integration: Advances in AI enhance candidate sourcing capabilities through predictive analytics.
- Partnerships: Collaborations with external platforms broaden sourcing options.
Threats:
- Changing Trends: Shifts in candidate behavior may impact the effectiveness of traditional sourcing methods.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to changing data protection regulations poses compliance challenges.
3.1.3 Candidate Screening
Strengths:
- Centralized Data: Systems offer a centralized repository, streamlining candidate information for better organization and accessibility.
- Automation: Automated tracking processes reduce manual data entry, enhancing accuracy.
Weaknesses:
- User Interface Issues: Complex interfaces may impede user experience and slow down application tracking.
- Overreliance on Automation: Excessive reliance may overlook nuanced candidate considerations.
Opportunities:
- Mobile Accessibility: Expanding mobile access improves flexibility for recruiters managing applications on the go.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implementing effective feedback enhances the applicant tracking process.
Threats:
- Data Security: Ensuring candidate data security against cyber threats is an ongoing concern.
- Integration Challenges: Difficulty in integrating with other HR tools may hinder seamless applicant information flow.
3.1.4 Candidate Assessment
Strengths:
- Structured Evaluation: HCM systems ensure fair and consistent assessments through structured processes.
- Efficiency Through Automation: Automated assessment tasks save time and reduce manual effort.
Weaknesses:
- Limited Personalization: Some HCM systems may lack flexibility in personalizing assessments for specific roles or candidate profiles.
- Potential Bias in Algorithms: Automated assessments may carry biases, necessitating continuous monitoring and adjustment.
Opportunities:
- Advanced Analytics: Leveraging analytics within HCM systems provides deeper insights into candidate performance.
- Integration with Skill Testing Platforms: Collaborations with external skill testing platforms enhance assessment variety and accuracy.
Threats:
- Candidate Experience Concerns: Overly complex assessments may negatively impact the candidate experience.
- Security and Privacy Risks: Ensuring the security and privacy of candidate assessment data is crucial amid evolving data protection regulations.
3.1.5 Interview Scheduling
Strengths:
- Automated scheduling improves recruitment efficiency.
- Centralized communication streamlines interactions among recruiters, candidates, and teams.
Weaknesses:
- Challenges in dealing with varying availability may cause delays.
- Excessive automated communication can lead to information overload.
Opportunities:
- AI-driven scheduling optimizes interview coordination for efficiency.
- Advancements in virtual interview tools enhance the interview experience.
Threats:
- Technical issues may disrupt virtual interviews or automated scheduling.
- User resistance hinders successful implementation, emphasizing the need for effective change management.
3.1.6 Reference Check
Strengths:
- Automation: Automated reference check processes streamline the verification of candidate references, saving time and reducing manual effort.
- Standardization: HCM systems ensure standardized reference check procedures, contributing to consistency and accuracy.
Weaknesses:
- Limited Personalization: Some systems may lack flexibility in personalizing reference checks for specific roles or industries.
- Dependency on Reference Responsiveness: The effectiveness of reference checks may be hindered by delays or unresponsiveness from referees.
Opportunities:
- Integration with Feedback Systems: Collaborating with feedback systems can enhance the depth and quality of reference check insights.
- Advanced Analytics: Leveraging analytics within HCM systems can provide deeper insights into reference feedback.
Threats:
- Privacy Concerns: Ensuring privacy compliance during reference checks is crucial amid evolving data protection regulations.
- Technology Challenges: Technical issues during automated reference checks may disrupt the process, necessitating robust support measures.
3.1.7 Initiate Offer
Strengths:
- Automation: Automated offer initiation processes streamline the creation and delivery of job offers, saving time and reducing manual tasks.
- Accuracy: HCM systems contribute to accurate offer details, minimizing errors in the initiation process.
Weaknesses:
- Complexity: Some systems may have complex interfaces, potentially hindering user experience during the offer initiation process.
- Communication Delays: Dependencies on multiple approval stages may lead to delays in finalizing and initiating job offers.
Opportunities:
- Integration with E-Signature Platforms: Collaborating with e-signature platforms can enhance the speed and efficiency of offer acceptance.
- Personalization: Enhancing system flexibility for personalized offer details can cater to specific candidate preferences.
Threats:
- Data Security: Ensuring the security of sensitive offer-related information is crucial to mitigate risks of data breaches.
- User Resistance: Resistance to adopting new offer initiation methods may hinder successful implementation, emphasizing the need for effective change management.
3.1.8 Background check
Strengths:
- Automation: Automated background check processes streamline verification, saving time and reducing manual effort for recruiters.
- Compliance: HCM systems contribute to compliance with regulations by ensuring standardized and thorough background checks.
Weaknesses:
- Delayed Results: The effectiveness of background checks may be impacted by delays in receiving information from external agencies.
- Limited Customization: Some systems may have limitations in tailoring background checks to specific roles or industry requirements.
Opportunities:
- Integration with Verification Services: Collaborating with external verification services enhances the depth and accuracy of background checks.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implementing ongoing monitoring processes can provide real-time updates on candidate background information.
Threats:
- Privacy Concerns: Ensuring privacy compliance during background checks is crucial amid evolving data protection regulations.
- Technology Challenges: Technical issues during automated background checks may disrupt the process, necessitating robust support measures.
3.2. Analyzing the Candidate's Experience
3.2.1 Job Discovery
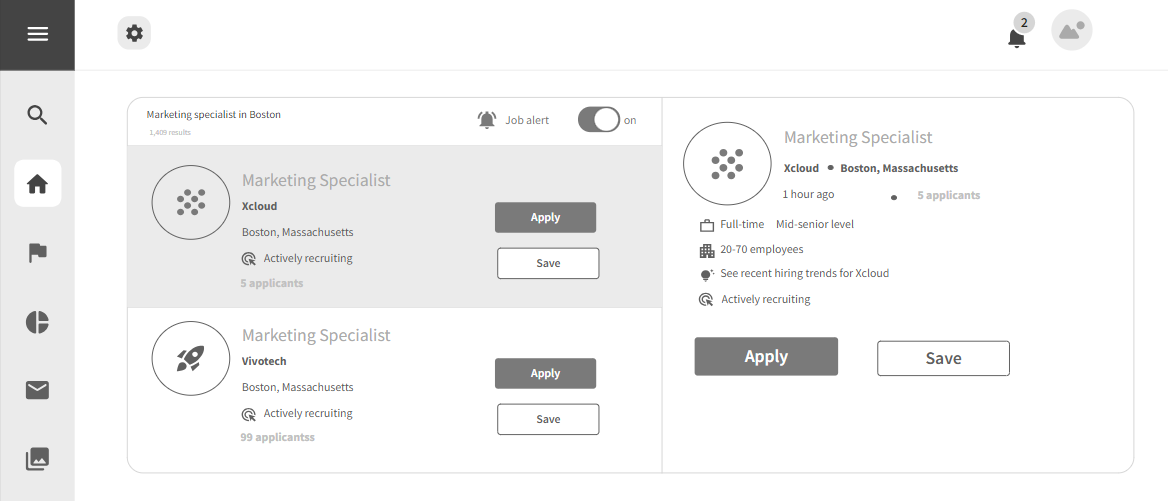
Strengths:
- Clear Job Descriptions: Candidates can easily understand job requirements and responsibilities.
- User-Friendly Navigation: Intuitive platform design facilitates smooth job exploration.
Weaknesses:
- Limited Personalization: Job recommendations may lack personalization based on individual preferences or skills.
- Information Overload: Extensive job listings might overwhelm candidates with too many options.
Opportunities:
- AI Integration: Integrate AI algorithms to provide personalized job suggestions tailored to candidates' profiles.
- Enhanced Filtering: Implement advanced filters to help candidates refine job searches based on specific criteria.
Threats:
- Potential Overlook: Candidates might overlook relevant opportunities due to the sheer volume of job listings.
- Competitive Listings: A crowded job board may make it challenging for certain positions to stand out.
3.2.2 Application Submission
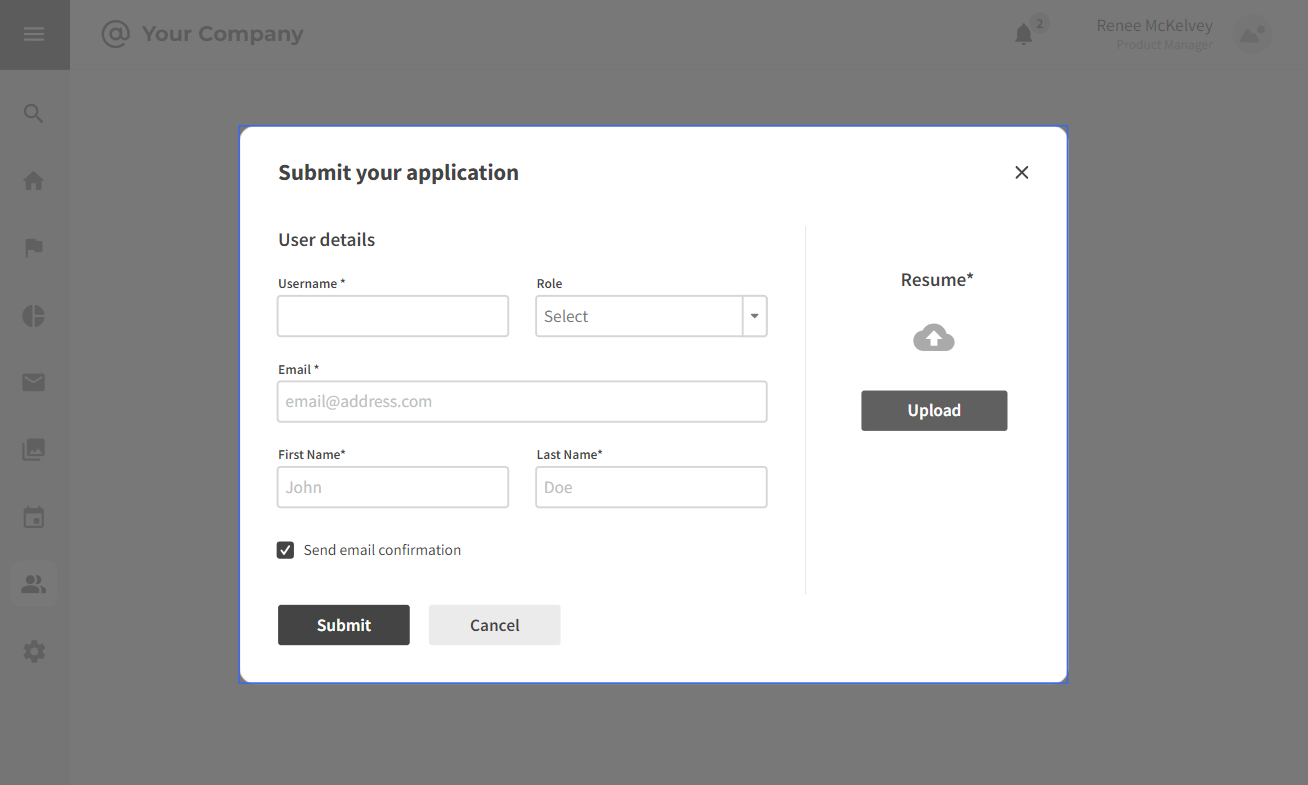
Strengths:
- Clear Job Descriptions: Candidates can easily understand job requirements and responsibilities.
- User-Friendly Navigation: Intuitive platform design facilitates smooth job exploration.
Weaknesses:
- Limited Personalization: Job recommendations may lack personalization based on individual preferences or skills.
- Information Overload: Extensive job listings might overwhelm candidates with too many options.
Opportunities:
- AI Integration: Integrate AI algorithms to provide personalized job suggestions tailored to candidates' profiles.
- Enhanced Filtering: Implement advanced filters to help candidates refine job searches based on specific criteria.
Threats:
- Potential Overlook: Candidates might overlook relevant opportunities due to the sheer volume of job listings.
- Competitive Listings: A crowded job board may make it challenging for certain positions to stand out.
3.2.3 Application Tracking
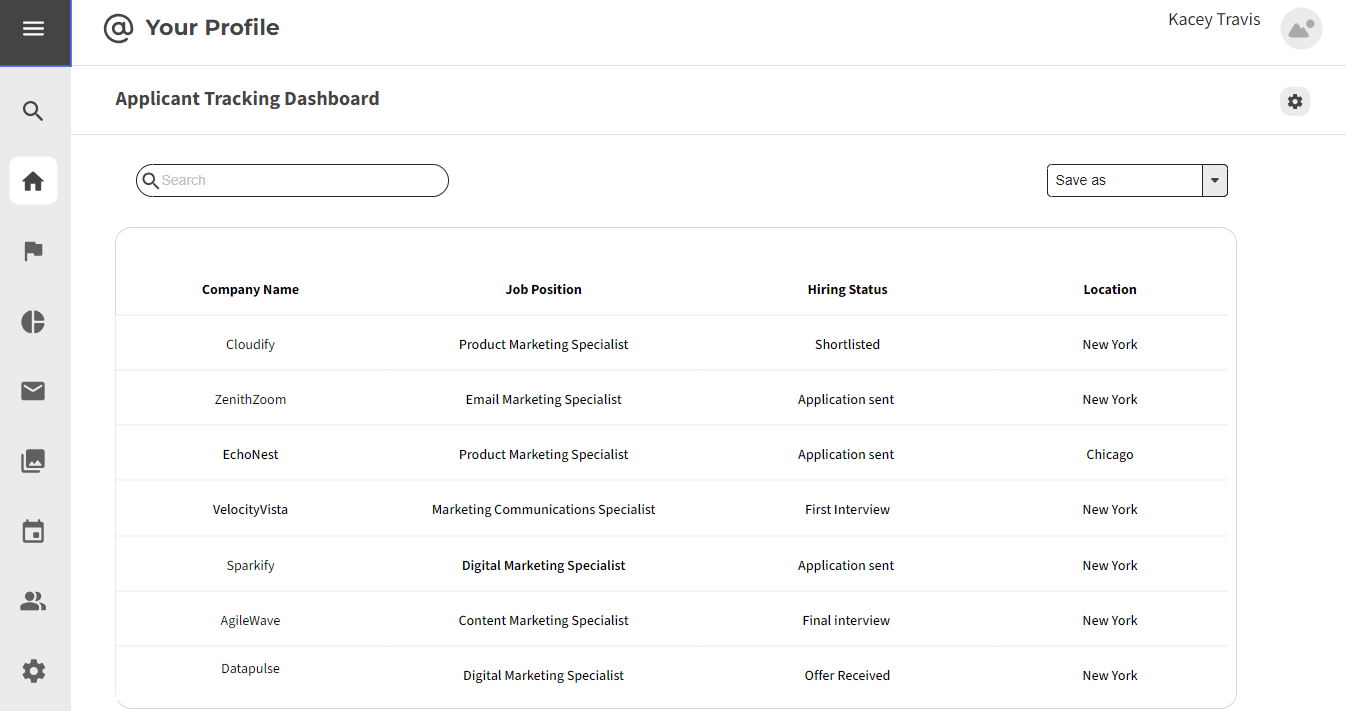
Strengths:
- Automated Application Updates: HCM systems offer automated application tracking, keeping candidates informed about the status of their applications.
- Centralized Communication: Candidates can receive and respond to communication within the HCM platform, ensuring a centralized and organized experience.
Weaknesses:
- Automated Responses Limitations: Over-reliance on automated responses may lack the personal touch needed for certain candidate communications.
- Communication Delays: Candidates may experience delays in receiving updates, especially in fast-paced recruitment processes.
Opportunities:
- Interactive Application Tracking: Incorporating interactive features for candidates to engage with their application status can enhance the experience.
- AI-Driven Communication: Integration of AI for personalized candidate communication can improve engagement.
Threats:
- Overcommunication: Excessive automated communication may lead to candidate disengagement.
- Lack of Transparency: Insufficient information about the application process can lead to frustration among candidates.
3.2.4 Interview Process
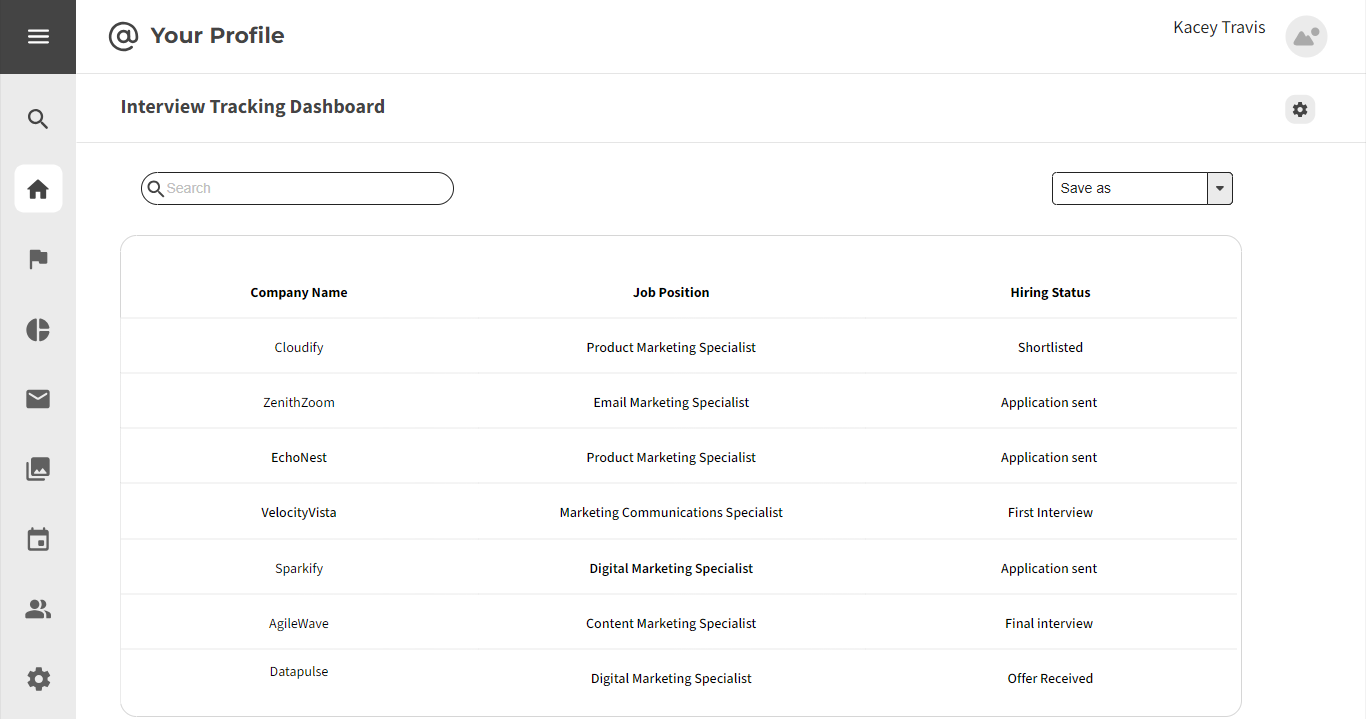
Strengths:
- Automated Interview Scheduling: HCM systems facilitate automated interview scheduling, reducing manual coordination efforts for candidates.
- Virtual Interview Capabilities: The integration of virtual interview tools allows candidates to participate in interviews remotely.
Weaknesses:
- Technical Difficulties: Virtual interview tools may pose technical challenges for some candidates, impacting their interview experience.
- Limited Interview Format Options: Lack of flexibility in interview formats may not cater to diverse candidate preferences.
Opportunities:
- Virtual Interview Preparation Resources: Providing resources and guidelines for virtual interviews can enhance candidate preparedness.
- Interview Format Choices: Offering choices in interview formats (virtual, in-person) can accommodate varying candidate preferences.
Threats:
- Candidate Comfort: Candidates may experience discomfort or unfamiliarity with virtual interviews, affecting their performance.
- Scheduling Conflicts: Automated scheduling may clash with candidates' availability, leading to scheduling conflicts.
3.2.5 Assessment and Testing
Strengths:
- Convenient Evaluation: Seamless in-platform assessments provide candidates with a user-friendly experience.
- Objective Measurement: Automated assessments contribute to objective evaluations, minimizing bias.
Weaknesses:
- Limited Variety: Some platforms may offer a restricted range of assessment types, limiting the diversity of evaluation methods.
- Potential Bias: Automated assessments may carry inherent biases, necessitating continuous monitoring and adjustment.
Opportunities:
- Integration with Diverse Testing Platforms: Collaborations with external testing services can broaden the variety and accuracy of assessments.
- Adaptive Testing: Implementing adaptive testing features based on candidate performance can enhance accuracy.
Threats:
- Technical Challenges: Technical issues during assessments, such as system glitches or connectivity problems, may disrupt the evaluation process.
- Privacy Concerns: Ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of candidate assessment data is crucial amid evolving data protection regulations.
3.2.6 Background Verification
Strengths:
- Streamlined Process: Background checks are initiated and conducted seamlessly through the HCM platform.
- Transparency: Real-time updates ensure transparency, keeping the candidate informed at every stage.
Weaknesses:
- External Dependency: Delays may occur due to the dependency on external verification agencies.
- Limited Personalization: Some systems may lack flexibility in tailoring checks to specific roles or industries.
Opportunities:
- Integration with Fast Services: Collaborating with efficient verification services can enhance the speed of the process.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implementing ongoing monitoring processes can provide real-time updates on candidate background information.
Threats:
- Privacy Concerns: Ensuring privacy compliance during background checks is crucial amid evolving data protection regulations.
- Technology Challenges: Technical issues during automated background checks may disrupt the process, necessitating robust support measures.
3.2.7 Offer Initiation

Strengths:
- Automation: Automated processes streamline the creation and delivery of job offers, ensuring efficiency.
- Accuracy: HCM systems contribute to accurate offer details, minimizing errors in the initiation process.
Weaknesses:
- Complexity: Some systems may have complex interfaces, potentially hindering the user experience during the offer initiation process.
- Communication Delays: Dependencies on multiple approval stages may lead to delays in finalizing and initiating job offers.
Opportunities:
- Integration with E-Signature Platforms: Collaborating with e-signature platforms can enhance the speed and efficiency of offer acceptance.
- Personalization: Enhancing system flexibility for personalized offer details can cater to specific candidate preferences.
Threats:
- Security: Ensuring the security of sensitive offer-related information is crucial to mitigate risks of data breaches.
- User Resistance: Resistance to adopting new offer initiation methods may hinder successful implementation, emphasizing the need for effective change management.
4.Building an AI-powered HCM using HrFlow.ai
In this era of digital transformation, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into HCM emerges as a game-changer, offering unprecedented opportunities for efficiency, personalization, and strategic decision-making.
Here are the transformative steps of building an AI-powered HCM with HrFlow.ai.
4.1 AI-powered HCM for Recruiters
4.1.1 Job Requisition
- HrFlow.ai automates the pre-filling of job offer fields with Tagging API, reducing the learning curve and enhancing efficiency.
4.1.2 Candidate Review
- HrFlow.ai's resume parsing facilitates better candidate-job matching and seamlessly integrates parsed job details into your workflow for productivity.
- HrFlow.ai’s Resume Parser API includes text parsing, extracting parsed document objects according to each recruiter’s specific needs, to parse resumes.
4.1.3 Candidate Screening
- Relevant screening with AI searching and Matching: HrFlow.ai's Searching and Scoring APIs can be leveraged for AI-driven search and matching, ensuring relevant candidate screening.
- HrFlow.ai's Tagging API allows the assessment of soft skills and cultural fit by analyzing candidates' profiles and experiences.
- Save time and reduce unqualified applications: HrFlow.ai's Searching and Scoring APIs can efficiently filter out unqualified applications, saving valuable time for recruiters.
4.1.4 Candidate Assessment
- HrFlow.ai's Tagging API assesses soft skills and cultural fit, providing a holistic view beyond traditional assessments.
- HrFlow.ai's Text Parsing, Resume Parsing, and Tagging APIs can automatically update and enrich candidate contact information.
- HrFlow.ai's various connectors allow integration with communication platforms for streamlined candidate engagement.
4.1.5 Interview Scheduling
- Set up the various HrFlow.ai Connectors to streamline the scheduling interview process with candidates.
- Incorporate HrFlow.ai Workflows ensuring a smooth and engaging experience for both recruiters and candidates in interview scheduling.
4.1.6 Reference Check
- Leverage HrFlow.ai connectors to minimize delays or unresponsiveness from referees through reminders and optimized timing.
- Automate with HrFlow.ai workflows tailoring reference check questions based on the unique requirements of each role.
4.1.7 Initiate Offer
- HrFlow.ai Text parsing extracts the needed candidate's data to personalize offer details based on individual candidate needs, creating a more tailored and appealing offer.
- Integrate HrFlow.ai with e-signature platforms, allowing for seamless and efficient offer acceptance. This integration enhances the speed and security of the acceptance process.
4.1.8 Background check
- Optimize background checks by exploring automated features within HrFlow.ai Workflows.
- HrFlow.ai's Tagging API can automatically extract and check information from various data sources.
4.2 AI-powered HCM for Candidates
3.2.1 Job Discovery
- Implement HrFlow.ai's Job Searching API for rapid and relevant job discovery. Intelligent job recommendations using AI: The HrFlow.ai Talent Copilot can provide intelligent job recommendations tailored to candidates' profiles and preferences.
- Enhanced search based on experience and interests: HrFlow.ai's Searching API, integrated with the Rating and Tracking APIs, can offer an enhanced search experience based on a candidate's interests and experience.
3.2.2 Application Submission
- HrFlow.ai's Resume Parsing and Tagging APIs can automatically fill in application fields, reducing manual entry for candidates.
- HrFlow.ai's various connectors enable a simplified job application process through seamless integrations with 200+ connectors.
- HrFlow.ai's Tracking API and Workflows can be configured to provide status updates and notifications about application progress.
3.2.3 Application Tracking
- HrFlow.ai's Workflows introduce interactive features, ensuring timely updates and personalized candidate engagement.
3.2.4 Interview Process
- HrFlow.ai's system integrates with scheduling tools to organize and streamline interviews, ensuring an organized and efficient interview process.
- HrFlow.ai enhances the interview process by providing tools for collecting actionable feedback and aiding recruiters in making informed decisions.
3.2.5 Assessment and Testing
- Job Parsing and Tagging API from HrFlow.ai automates application field completion, minimizing manual entry for candidates during the talent application process.
3.2.6 Background Verification
- Use HrFlow.ai's various connectors to maintain accurate and up-to-date references.
- HrFlow.ai solutions are fully compliant with GDPR . Moreover, HrFlow.ai recently became the first and only AI solution for processing Talent and Workforce data recognized and cited as a reference by the European Union in its new law on AI risks and personal data protection.
- With HrFlow.ai, you can automate consent management, ensuring compliance with GDPR.
3.2.7 Offer Initiation
- Integrate HrFlow.ai with e-signature platforms to facilitate seamless and quick offer acceptance. This integration enhances the speed and efficiency of the overall offer initiation process, reducing manual steps and delays.
- HrFlow.ai safeguards sensitive data and ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
5. How to Choose The Right HCM For You
Identify Needs and Goals:
- Understand current challenges and future goals in human capital management.
- Consider budget, ease of use, customization options, and reporting needs.
- Evaluate cloud-based vs. on-premise options.
Research and Evaluate Options:
- Explore features and functionality, customization, ease of use, scalability, and security.
- Assess integration capabilities and overall implementation cost.
Run a Rigorous Demo Process:
- Prepare specific questions.
- Request a customized demo focused on your needs.
- Evaluate user experience, integration, and scalability.
- Assess vendor presentation and responsiveness.
Compare Features and Benefits:
- Evaluate customer support, industry relevance, integration, intuitiveness, scalability, and advanced features.
- Assess the system's ability to manage contingent workers and incorporate AI elements.
Test and Implement the Software:
- Develop a comprehensive test plan.
- Conduct testing in a sandbox environment.
- Involve employees in testing.
- Secure stakeholder buy-in, provide robust training, offer ongoing support, and communicate benefits for adoption.
Drive Widespread Adoption:
- Secure stakeholder buy-in.
- Provide tailored training and ongoing support.
- Communicate tangible benefits for user understanding and motivation.
6.Conclusion and Key Takeaways
- Innovation at the Core: The integration of HrFlow.ai's Tagging API forms the foundation, injecting innovation at the core of your Human Capital Management (HCM) system. This sets the stage for an intelligent, adaptive, and forward-thinking approach.
- Revolutionizing Candidate Sourcing: With HrFlow.ai's Talent Funnels API, transform the way you source talent. Connect effortlessly to diverse pools, and leverage advanced Searching and Scoring capabilities for pinpoint accuracy in candidate selection.
- Seamless Automation in Candidate Tracking: HrFlow.ai's Workflow APIs optimize and automate every step of the candidate tracking process. From application to evaluation, experience a seamless journey that enhances efficiency and decision-making.
- Intelligent Interview Coordination: The Recruiter Copilot API from HrFlow.ai redefines interview scheduling, infusing intelligence into coordination based on participant availability. Eliminate complexities and foster a smooth, intelligent interview experience.
- Holistic Candidate Evaluation: Utilize HrFlow.ai's Tagging API to go beyond traditional evaluation methods. Assess soft skills and cultural fit with precision, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of each candidate's potential and fit within the organization.

