Summary
This case study encapsulates the journey of AI LMS, outlining challenges, and spotlighting the role of AI in revolutionizing modern training practices and e-learning.
- Evolution of LMS Landscape: Explores the historical context and current market dynamics of Learning Management Systems (LMS) in response to the increasing demand for effective training.
- Challenges with Traditional LMS: Highlights limitations of traditional LMS solutions, addressing issues related to scalability, accessibility, and personalized learning experiences for diverse audiences.
- Entrance of AI: Introduces the transformative impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) with HrFlow.ai in LMS, emphasizing personalized learning journeys, automated assessments, and real-time insights.
- Shift towards Efficiency: Illustrates the transformative potential of AI in reshaping training and development strategies, steering organizations towards more adaptive, efficient, and impactful learning initiatives.
Table of contents:
- Overview
1.1 Abstract - History and Market Landscape of LMS
2.1 Key drivers of the expanding LMS market
2.2 Top leading LMS solutions in the 2023 market
2.3 LMS Businesses' Primary Revenue Stream - User Experience with Traditional LMS
3.1. Analyzing the Recruiter's Experience
3.2. Analyzing the Candidate's Experience - Building an AI-powered LMS using HrFlow.ai
4.1 AI-powered LMS for Recruiters
4.2. AI-powered LMS for Candidates - How To Choose The Right LMS For You
- Conclusion and Key Takeaways
1.Overview
1.1 Abstract
In the fiercely competitive landscape of talent acquisition, Learning Management Systems (LMS) are emerging as crucial tools for organizations seeking to enhance training and development strategies. This case study delves into the rapid adoption of LMS over recent years, as organizations aim to optimize learning processes, boost employee skills, and meet evolving business demands.
LMS platforms are designed to centralize and streamline learning experiences for both recruiters and candidates. By consolidating training materials, facilitating course delivery, and tracking progress, LMS systems empower organizations to efficiently manage training initiatives. They address challenges related to scalability, accessibility, and tracking candidates' engagement, providing a comprehensive solution for diverse learning needs.
However, as organizations navigate the evolving landscape of training and development, traditional LMS solutions are encountering limitations. Users often find them lacking in terms of personalization, real-time insights, and adaptability to different learning styles.
Enter artificial intelligence (AI). The next frontier in Learning Management Systems harnesses AI capabilities to revolutionize the learning experience for both educators and learners. AI LMS solutions promise personalized learning journeys, automated assessments, and insights that empower organizations to tailor training programs for maximum impact.
This case study unravels the evolution of Learning Management Systems and how the infusion of AI is reshaping e-learning and development strategies. The case study dissects the key advantages of AI-powered LMS for both recruiters and candidates, illuminating how these advancements aim to make training more adaptive, efficient, and impactful in today's dynamic organizational landscape.
2.History and Market Landscape of LMS
The global Learning Management System (LMS) market is expected to grow from $18.7 billion in 2022 to $43.6 billion by 2027, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.4%.
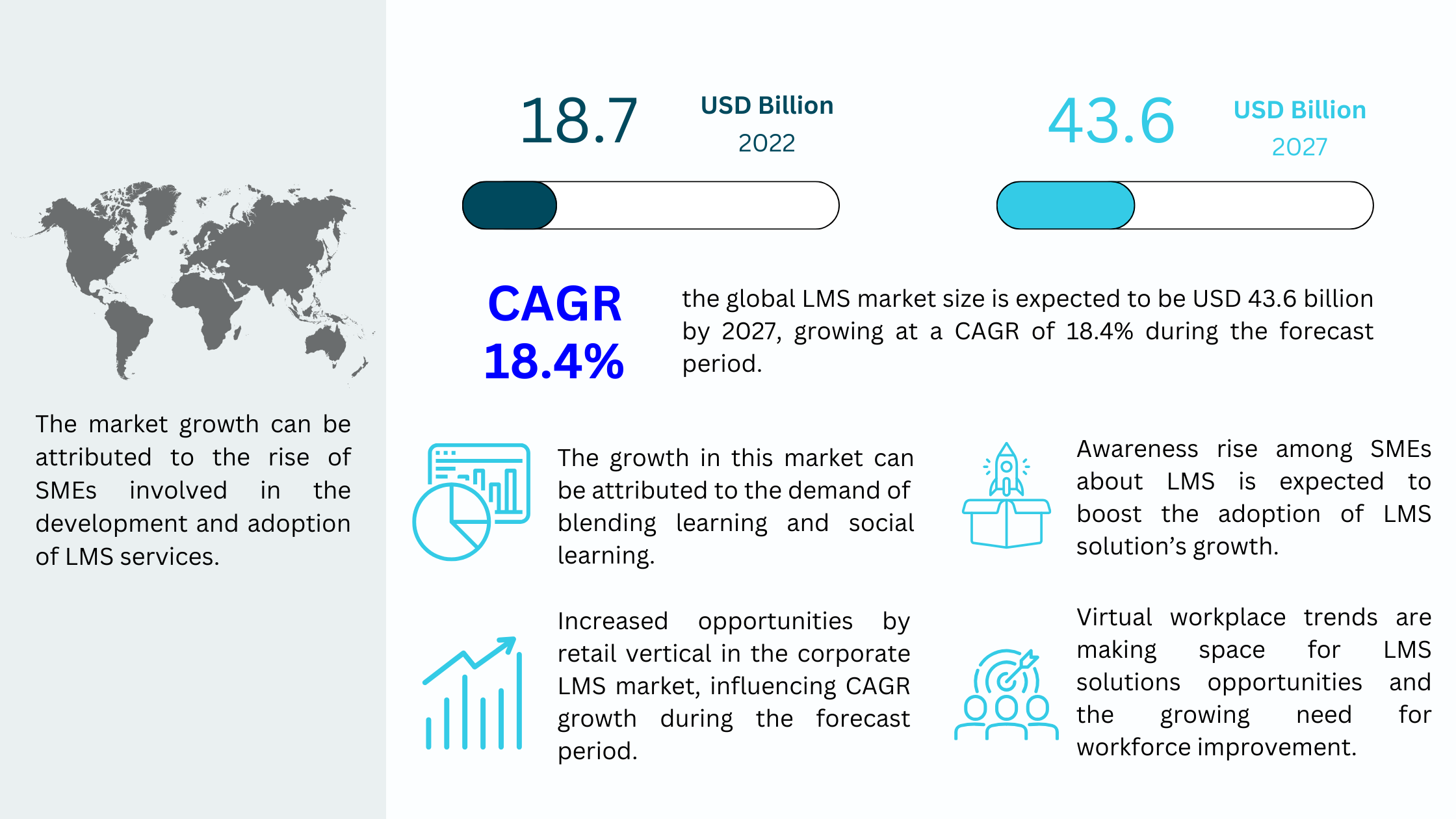
2.1 Key drivers of the expanding LMS market
Several key trends are shaping the landscape of the LMS market:
- A surge in online learning demand: The COVID-19 pandemic has hastened the transition to online education, leading to a heightened need for LMSs.
- Growing preference for cloud-based LMSs: Cloud-based solutions are gaining prominence due to their scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional on-premises LMSs.
- Ascendance of mobile learning: The increasing use of mobile devices for educational purposes is fueling the demand for LMSs that seamlessly integrate with mobile platforms.
2.2 Top leading LMS solutions in the 2023 market
Google Classroom:
- Overview: Google Classroom is a free, web-based platform designed for schools. It simplifies the creation, distribution, and grading of assignments in a paperless way.
- Target: Educational institutions, teachers, and students.
Canvas LMS:
- Overview: Canvas LMS is a robust learning management system used for online and blended learning. It offers customizable course structures and collaborative tools.
- Target: Educational institutions, K-12 schools, and higher education.
Docebo:
- Overview: Docebo is a cloud-based LMS that focuses on corporate training. It provides features like e-learning, social learning, and analytics.
- Target: Businesses and enterprises for employee training.
Moodle:
- Overview: Moodle is an open-source LMS used for creating and managing online courses. It offers flexibility and customization options.
- Target: Educational institutions, businesses, and organizations.
Coursera:
- Overview: Coursera is an online learning platform that offers a wide range of courses and degrees in collaboration with universities and organizations.
- Target: Individual learners, professionals, and organizations for upskilling.
iSpring Learn:
- Overview: iSpring Learn is a cloud-based LMS that focuses on simplicity and e-learning content creation.
- Target: Businesses and organizations for employee training.
2.3 LMS Businesses' Primary Revenue Stream
In the Learning Management System (LMS) market, businesses primarily generate revenue through the following streams:
- Fees: Charging users, typically organizations or educational institutions, a subscription fee for accessing and using the LMS platform. Fees may be based on the number of users, features, or usage.
- License Fees: Selling software licenses to organizations for the installation and use of the LMS platform. This model often involves an upfront payment or periodic licensing fees.
- Course Sales: Generating revenue by offering and selling premium courses or specialized content within the LMS platform. Users pay for access to specific educational content.
- Professional Services: Providing additional services such as customization, integration, training, and support. Businesses charge fees for these services to enhance the LMS implementation.
- Enterprise Solutions: Offering advanced or enterprise-level versions of the LMS with additional features, scalability, and support. Businesses charge a premium for these more comprehensive solutions.
- Consulting Services: Providing consulting services to assist organizations in optimizing their use of the LMS, including strategic planning, content development, and performance analysis.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Forming partnerships with content providers, educational institutions, or other organizations and earning a share of revenue from joint ventures, collaborations, or shared content sales.
- Renewal Fees: Charging recurring fees for subscription renewals, ensuring ongoing access to the LMS platform and its features.
3. User Experience with Traditional LMS
User Experience with traditional Learning Management Systems (LMS) can vary depending on the specific platform and its features. Traditional LMS platforms were often designed with a focus on delivering and managing training content. Here are some common aspects of the user experience with traditional LMS.
3.1 Analyzing the Recruiter Experience
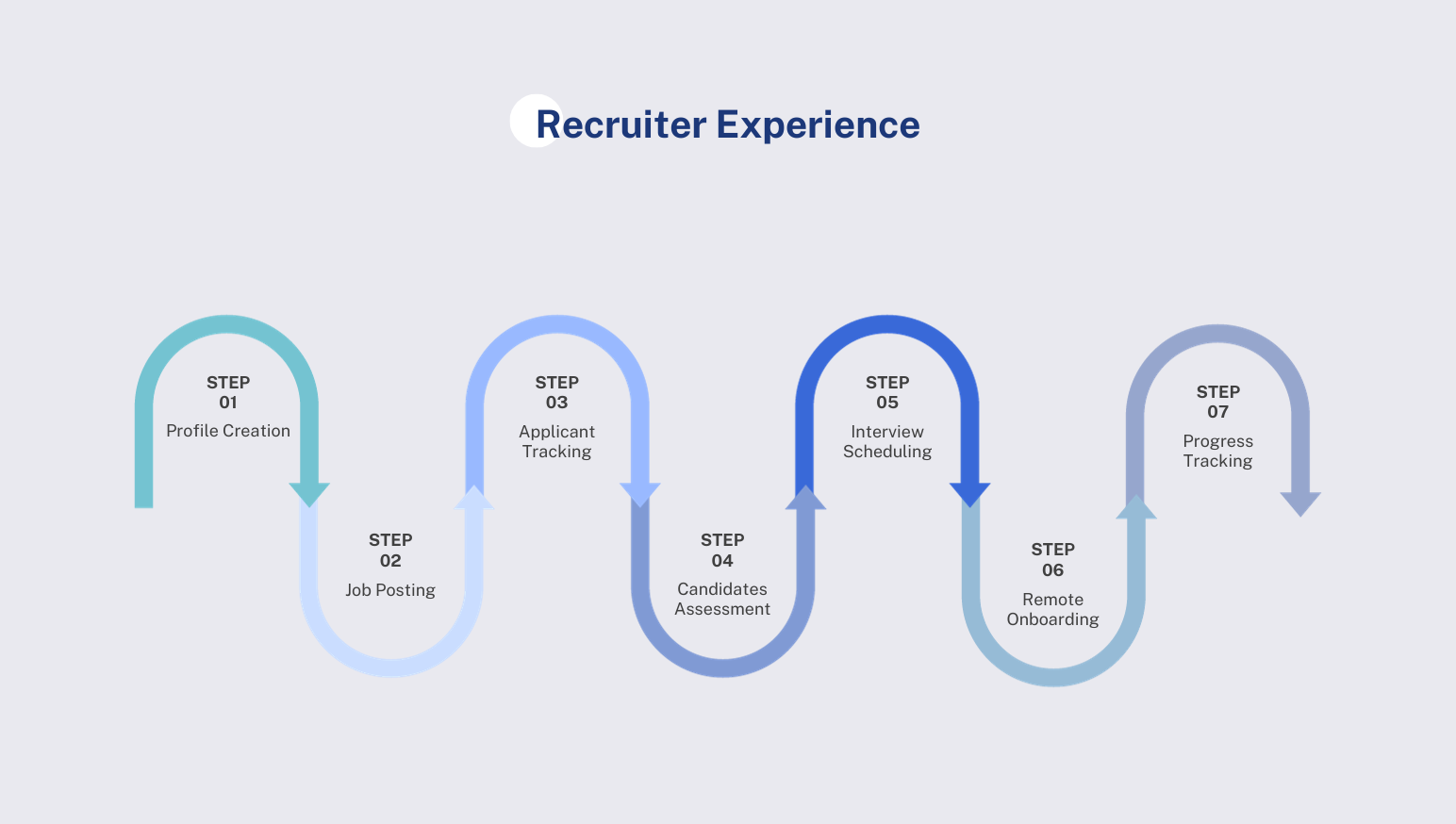
3.1.1 Profile Creation
Strengths
- Provides a centralized and structured view of recruiters' professional information.
- Can contribute to a sense of community and collaboration among recruiters.
Weaknesses
- The process may be time-consuming, potentially leading to incomplete profiles.
- Limited flexibility in customization may result in generic profiles.
Opportunities
- Profiles can serve as a valuable resource for talent acquisition teams looking to identify suitable recruiters.
- Integration with recruitment systems can enhance efficiency in the hiring process.
Threats
- Privacy concerns and data security issues may deter recruiters from creating detailed profiles.
- Resistance to adoption may result in incomplete or outdated profiles, limiting their usefulness.
3.1.2 Job Posting
Strengths
- Efficient dissemination of job information to a wide audience.
- Ability to tailor job postings based on specific requirements.
Weaknesses
- Dependency on the effectiveness of the LMS in reaching the target audience.
- Limited personalization compared to other advertising methods.
Opportunities:
- Integration with social media or external job boards for broader reach.
- Analytical tools within the LMS can provide insights into the performance of job postings.
Threats
- Competition for attention on popular job platforms.
- Changes in algorithms affect the visibility of job postings.
3.1.3 Applicant Tracking
Strengths
- Centralized tracking for all applicants in one system.
- Real-time updates on candidate statuses for recruiters.
Weaknesses
- Possible data overload if not managed effectively.
- Dependence on accurate data input by recruiters.
Opportunities
- Integration with other HR tools for a seamless hiring workflow.
- Customizable reporting features for analysis and decision-making.
Threats
- Technical issues or system downtimes impact tracking accuracy.
- Potential resistance from users if the system is not user-friendly.
3.1.4 Candidates Assessment
Strengths
- Standardized assessments for fair candidate evaluation.
- Immediate results and feedback can expedite decision-making.
Weaknesses
- Risk of candidates gaming the system with well-rehearsed answers.
- Limited ability to assess certain soft skills through automated tests.
Opportunities
- Continuous improvement based on analytics and feedback.
- Integration with simulation tools for more realistic assessments.
Threats
- Legal and ethical concerns regarding the fairness of assessments.
- Potential resistance from candidates if assessments are perceived as time-consuming.
3.1.5 Interview Scheduling
Strengths
- Streamlined coordination and scheduling process.
- Integration with calendar systems for convenience.
Weaknesses
- Dependency on accurate availability of information from all parties.
- Risk of technical glitches impacting scheduling accuracy.
Opportunities
- Automated reminder features to reduce no-shows.
- Integration with video conferencing tools for remote interviews.
Threats
- Miscommunication leads to scheduling conflicts.
- Dependence on stable internet connections for remote interviews.
3.1.6 Remote Onboarding
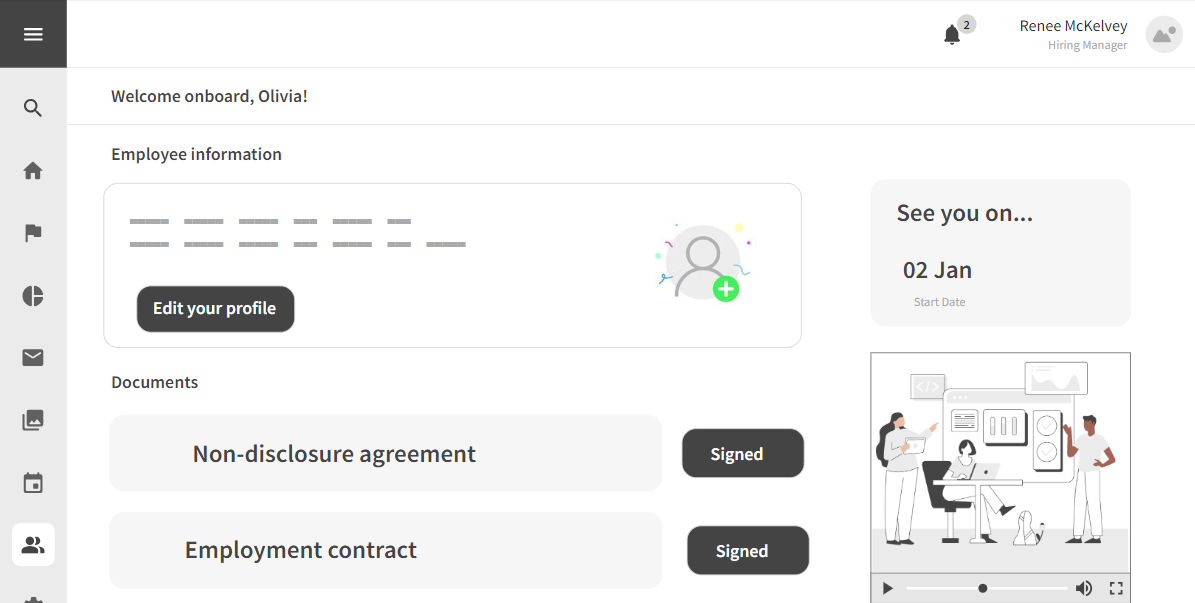
Strengths
- Efficient delivery of training materials through the LMS.
- Remote onboarding capabilities for geographically dispersed teams.
Weaknesses
- Potential challenges in ensuring engagement and participation in remote onboarding.
- Limited personalization in the onboarding process.
Opportunities
- Integration with collaboration tools for a more interactive onboarding experience.
- Continuous feedback mechanisms for ongoing improvement.
Threats
- Technical issues affecting the accessibility of onboarding materials.
- Employee disengagement if the onboarding process lacks a personal touch.
3.1.7 Progress Tracking
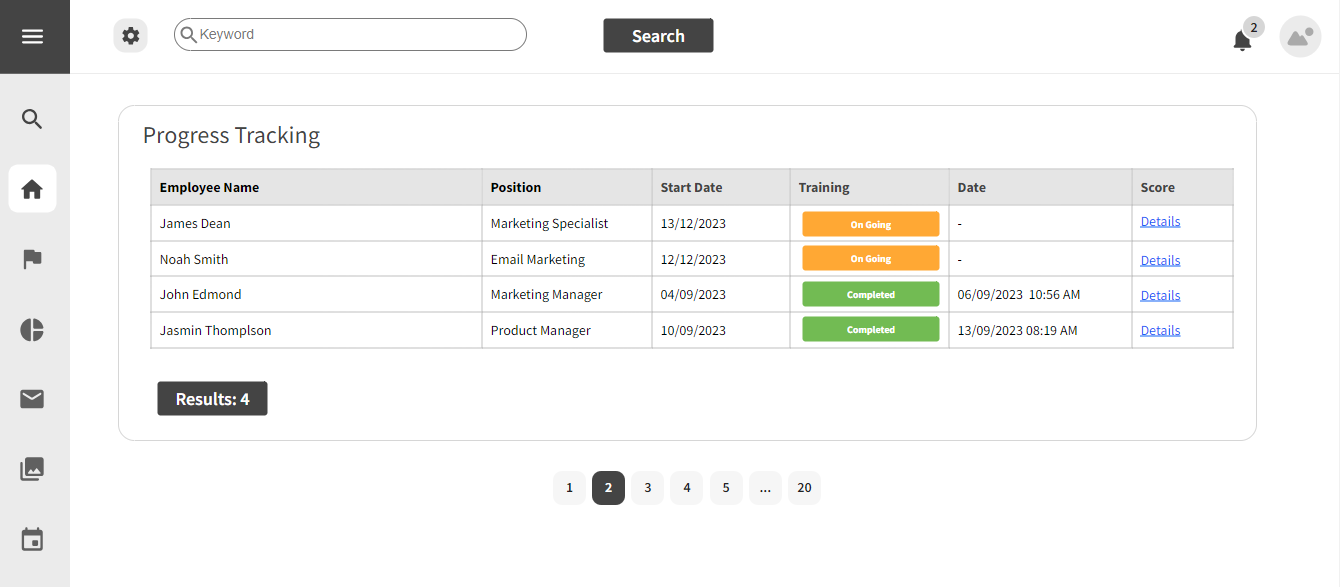
Strengths
- Real-time monitoring of candidate progress.
- Analytics for identifying trends and areas for improvement.
Weaknesses
- Overemphasis on quantitative metrics may overlook qualitative aspects of progress.
- Dependency on accurate data entry by trainers and candidates.
Opportunities
- Integration with performance management systems for a holistic view.
- Customizable dashboards for personalized progress tracking.
Threats
- Misinterpretation of data leading to incorrect decisions.
- Resistance from trainers or candidates if they perceive the tracking as invasive.
3.2 Analyzing the Candidate Experience
3.2.1 Profile Creation
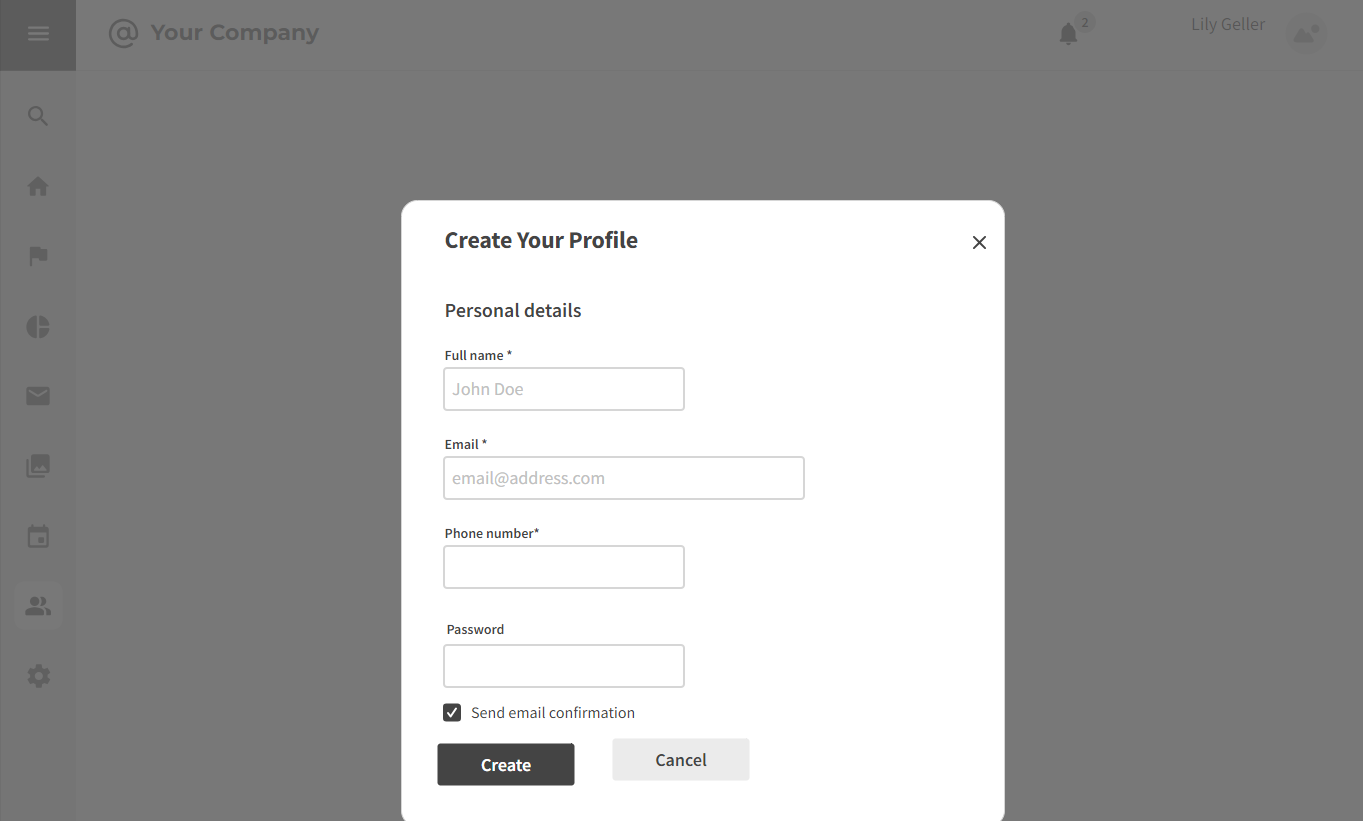
Strengths
- Provides a standardized format for capturing essential candidate details.
- Simplifies the onboarding process by centralizing initial information.
Weaknesses
- May lack personalization options for candidates to showcase unique attributes.
- Lengthy profile creation may result in candidate drop-offs.
Opportunities
- Opportunity to integrate with professional social profiles for seamless information import.
- Implementing customizable features for a more tailored profile.
Threats
- Potential threats related to data security and privacy concerns.
- Competition from platforms offering quicker onboarding processes.
3.2.2 Profile Building
Strengths
- Comprehensive Profiles and Holistic Candidate View.
- Provides a centralized and structured view of recruiters' professional information.
Weaknesses
- Time-Consuming and Data Accuracy.
- Additional effort required to input comprehensive details may lead to delays.
Opportunities
- Resume Integration and Skill Endorsements.
- Integration with recruitment systems can streamline the hiring process.
Threats
- Resistance to Detailed Profiles and Competing Priorities.
- Candidates may resist providing in-depth information.
3.2.3 Assessments
Strengths
- Objective Evaluation and Immediate Feedback.
- Provides an objective method for evaluating candidate knowledge.
Weaknesses
- Limited to Knowledge-Based Assessments and Potential Cheating.
- Challenges in assessing practical skills or soft skills.
Opportunities
- Gamified Assessments and Real-world Simulations.
- Introduction of gamified elements for increased engagement.
Threats
- Technology Dependence and Assessment Fatigue.
- Technical issues may disrupt the assessment process.
3.2.4 Progress Tracking
Strengths
- Transparency and Motivation.
- Real-time monitoring of candidate progress.
Weaknesses
- Overemphasis on Quantitative Metrics and Dependence on Data Accuracy.
- Relies on accurate data entry by trainers and candidates.
Opportunities
- Integration with Performance Management and Customizable Dashboards.
- Provides a centralized and structured view of recruiters' professional information.
Threats
- Misinterpretation of Data and Resistance to Tracking.
- Resistance from trainers or candidates if tracking is perceived as invasive.
3.2.5 Engagement

Strengths
- Enhanced Engagement and Knowledge Sharing.
- Promotes engagement through communication with instructors and peers.
Weaknesses
- Potential Information Overload and Limited Real-time Interaction.
- Excessive communication tools may lead to information overload.
Opportunities
- Integration with Collaboration Tools and Community Building.
- Integration with collaboration tools for a more interactive experience.
Threats
- Technical Glitches and Lack of Participation.
- Technical issues affecting the accessibility of communication tools.
3.2.6 Feedback and Evaluation
Strengths
- Continuous Improvement and User-Centric Development.
- Enables continuous improvement of content and delivery.
Weaknesses
- Biased Feedback and Resistance to Evaluation.
- Potential for biased or incomplete feedback from some candidates.
Opportunities
- Automated Feedback Surveys and Incentivized Feedback.
- Implementing automated feedback surveys for streamlined data collection.
Threats
- Lack of Actionable Insights and Negative Impact on User Experience.
- Poorly managed feedback processes may impact the overall user experience.
4. Building an AI-powered LMS using HrFlow.ai
Remodeling the traditional Learning Management Systems (LMS), advanced AI capabilities bring a paradigm shift, making training and development initiatives more adaptive, efficient, and impactful.
Leading this transformative wave is HrFlow.ai, spearheading the integration of cutting-edge AI solutions to elevate the next generation of LMS platforms.
HrFlow.ai stands out as a trailblazer, offering remarkable enhancements to traditional LMS software. Here are key improvements HrFlow.ai introduces to legacy LMS solutions:
4.1 AI-powered LMS for Recruiters
4.1.1 Profile Creation
- Implement HrFlow.ai's Job Searching API for rapid and relevant job discovery, reducing the time spent on the sign-up process.
- Leverage HrFlow.ai's Job Searching API and Talent Copilot to optimize the sign-up process for candidates using mobile devices.
- Integrate Text Linking to automate data retrieval, allowing candidates to effortlessly populate information and streamline the sign-up process.
4.1.2 Job Posting
- Automated job posting to relevant channels: HrFlow.ai Talent Funnels allows Recruiters to post their job offers to multiple channels thanks to its impressive library of 200+ connectors.
- HrFlow.ai can also help create custom workflows that follow specific business logic set up by the client.
4.1.3 Applicant Tracking
- Advanced searching and matching with AI: HrFlow.ai Recruiter Copilot offers recruiters advanced searching and resume scoring capabilities to source candidates efficiently.
4.1.4 Candidates Assessment
- HrFlow.ai's Tagging API assesses soft skills and cultural fit, providing a holistic view beyond traditional assessments.
- HrFlow.ai's Text Parsing, Resume Parsing, and Tagging APIs can automatically update and enrich candidate contact information.
- HrFlow.ai's various connectors allow integration with communication platforms for streamlined candidate engagement.
4.1.5 Interview Scheduling
- Set up the various HrFlow.ai Connectors to streamline the scheduling interview process with candidates.
- Incorporate HrFlow.ai Workflows ensuring a smooth and engaging interview scheduling experience for both recruiters and candidates.
4.1.6 Remote Onboarding
- Leverage HrFlow.ai connectors on learning management systems to automate and streamline the remote onboarding process and minimize error in manual data entry.
- Automate the remote onboarding with HrFlow.ai workflows to dodge the risk of delayed onboarding and compliance issues.
4.1.7 Progress Tracking
- HrFlow.ai candidates' Usage Reports help recruiters review applicants' volume and sources. Moreover, HrFlow.ai offers structured and comprehensive data about applicants, which helps provide the best insights about your candidates' progress.
4.2. AI-powered LMS for Candidates
4.2.1 Profile Creation
- Implement HrFlow.ai's Job Searching API for rapid time spent on the profile creation process.
- Leverage HrFlow.ai's Job Searching API and Talent Copilot to optimize the sign-up process for candidates using mobile devices.
- Integrate Text Linking to automate data retrieval, allowing candidates to populate information and streamline the profile creation process effortlessly.
4.2.2 Profile Building
- Utilize Talent Copilot for a seamless and secure profile-building process, overcoming platform limitations and ensuring data privacy.
4.2.3 Assessments
- Job Parsing and Tagging API from HrFlow.aiautomate automates assessment tracking for accurate data entry.
4.2.4 Progress Tracking
- The Job Parsing and Tagging API from HrFlow.aifeedback automate progress tracking, minimizing manual entry for candidates during this step of the process.
- HrFlow.ai's connectors simplify the progress tracking process by seamlessly integrating with 200+ connectors, facilitating the smooth submission of candidates’ progress.
4.2.5 Engagement
- Integrate external communication tools within HrFlow.ai Workflows to enable personalized messaging. Tailor your communication to specific managers.
4.2.6 Feedback and Evaluation
- Talent Copilot helps candidates to automate unbiased feedback and objective evaluations, indirectly contributing to a positive candidate journey in this stage.
- Leverage HrFlow.ai various connector to request feedback from recruiters.
5. How To Choose The Right LMS For You

Step 1: Identify Your Needs
- Establish specific criteria for selecting an LMS from over 600 options.
- Define training goals and break them down into specific, measurable, achievable, and time-limited tasks.
- Consider factors such as reducing certification time for sales representatives and ensuring staff proficiency in product knowledge and sales techniques.
- Understand your audience by answering key questions regarding their age, skill levels, technological familiarity, preferred study locations, and the scale of your training requirements.
Step 2: Outline Your LMS Requirements
- Focus on listing comprehensive LMS requirements based on learning goals, objectives, and audience demographics.
- Categorize requirements based on your business needs to ensure a thorough understanding of necessary features for your training strategy.
Step 3: Explore the Market
- Seek recommendations from colleagues.
- Check ratings and reviews on platforms like Capterra and G2Crowd.
- Utilize filtering tools to identify LMS options that align with your must-have features.
- Create a preliminary list of 10-15 platforms.
Step 4: Evaluate Vendors
- Browse vendor websites and review customer testimonials.
- Assess vendor experience, awards, and the quality of technical support and updates.
- Consider factors like localization features and system interface.
- Aim to create a shortlist of 3-5 vendors that closely match your requirements.
Step 5: Test the LMS
- Take advantage of free trials offered by LMS providers.
- Focus on user-friendliness, necessary features, and technical support responsiveness.
- Evaluate the system's ability to handle various materials and formats, ensuring it aligns with your training needs.
- Ask for use case demonstrations from the remaining 3-5 vendors.
6. Conclusion and Key Takeaways
In conclusion, the exploration of Learning Management Systems (LMS) in this case study underscores the pivotal role these platforms play in the dynamic landscape of organizational training and development. As the demand for effective learning solutions intensifies, traditional LMS solutions face challenges related to scalability, accessibility, and personalized learning experiences.
The infusion of Artificial Intelligence (AI), exemplified by HrFlow.ai, emerges as a transformative force, promising to revolutionize LMS capabilities. AI-powered LMS solutions hold the promise of personalized learning journeys, automated assessments, and real-time insights, marking a significant shift towards more adaptive, efficient, and impactful training initiatives.
Key Takeaways:
- Evolution of Learning Management Systems: The historical and market landscape of LMS reveals their pivotal role in centralizing and optimizing learning experiences for organizations.
- Challenges with Traditional LMS: Traditional LMS solutions face limitations, and understanding these challenges is crucial for organizations seeking enhanced training strategies.
- AI's Transformative Impact: The integration of AI, exemplified by HrFlow.ai, presents a transformative avenue, offering remarkable enhancements to traditional LMS software.
- Shift towards Efficiency and Personalization: The transformative potential of AI in reshaping training and development signifies a shift toward more adaptive, efficient, and personalized learning experiences for diverse audiences.
In navigating the evolving landscape of LMS, organizations can leverage AI-powered solutions to stay ahead, ensuring their training initiatives align with the demands of modern learning and development practices.

