Summary:
In this article, we'll outline how AI's ascent has revolutionized industries, particularly in HR tech. This transformation has redefined AI-powered CRM solutions, equipping recruiters with robust tools.
However, previously effective recruitment strategies now need reevaluation due to this shift. We'll explore the impact of HrFlow.ai's APIs on talent CRM platforms, delving into its effects on recruiters and candidates.
Table of contents
1. Overview
1.1 Abstract
2. History and Market Landscape of Talent CRM
2.1 Forecasts of Future Talent CRM Market's Growth
2.2 Top leading Talent CRM solutions in the 2023 market
2.3 Talent CRM Businesses' primary revenue stream
3. User Experience with Traditional Talent CRM
3.1 Analyzing the Steps in the Recruiter's Journey
3.2 Analyzing the Steps in the Candidate's Journey
4. Building an AI-powered Talent CRM using HrFlow.ai
4.1 Enhancing Talent CRM for Recruiters: HrFlow.ai's Key Improvements
4.2 Enhancing Talent CRM for Candidates: HrFlow.ai's Key Improvements
5. How to Choose the Right Talent CRM for you
- Conclusion and Key Takeaways
1. Overview
1.1 Abstract
AI's rise has caused an automation revolution in all industries, especially the HR tech one.
And this evolution has flipped the game for AI-powered CRM solutions specifically. Recruiters now have a powerful set of tools and features under their belts.
But at the same time, recruitment strategies that were once effective may no longer work, and recruiters must find new ways to reach and engage a wider audience.
In this article, we'll break down the science behind this AI uprise, how it gave us talent CRM platforms, and how it's affecting recruiters as well as candidates in the modern world of white-collar jobs.
2. History and Market Landscape of Talent CRM
Before virtual job fairs and video interviews became the "new normal".
Previously, the recruitment process was a daunting undertaking, beginning when a position became available.
The process involved posting job descriptions on various platforms, including company websites, newspapers, and online job portals, and then sifting through hundreds of resumes to shortlist suitable candidates.
The process was incredibly manual and involved a lot of administrative work.
But ever since the rapid changes, with AI-powered CRM solutions taking center stage, there has been a spike in the demand for solutions that offer automation, personalization, and data-driven insights.
2.1 Forecasts of Future Talent CRM Market's Growth
In 2023, worldwide spending on candidate relationship management software reached $52 billion and is forecast to achieve $139 billion in 2030.
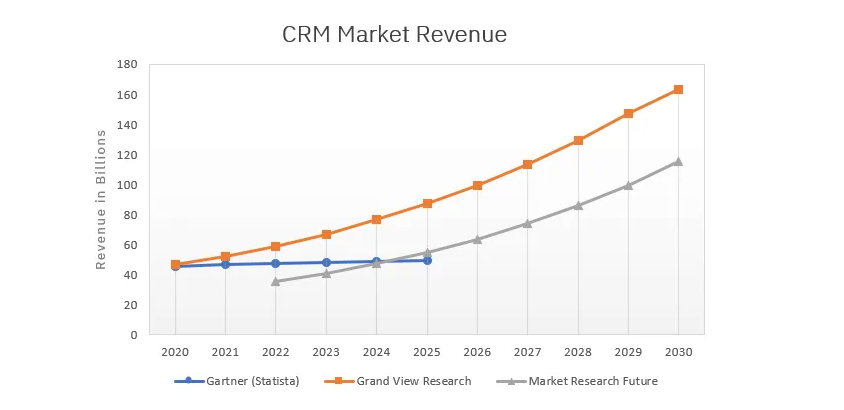
AI, as the driving force behind these CRM solutions, has become a vital component in talent acquisition, candidate management, and overall HR processes.
The utilization of AI in HR is not just a recent trend but a necessity, as it enables HR professionals to sift through bottomless tables of data, identify top talent, and provide a superior candidate experience.
While designed to simplify recruitment, Talent CRM had restricted functionalities, unable to comprehensively meet HR professionals' needs. This led to persistent manual tasks, creating a challenge for professionals trying to stay ahead in the recruitment process due to its overwhelming demands.
According to PWC, the primary catalysts driving the growth of CRM are digital transformation and the management of customer experiences.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) emerges as the pivotal technological force poised to significantly enhance CRM expansion. CRM providers are closely intertwining AI, machine learning, and natural language processing into their software applications.
2.2 Top leading Talent CRM solutions in the 2023 market
Several AI-powered CRM solutions have risen to prominence in the HR tech market, offering a range of features and functionalities that cater to the diverse needs of recruiters and HR teams.
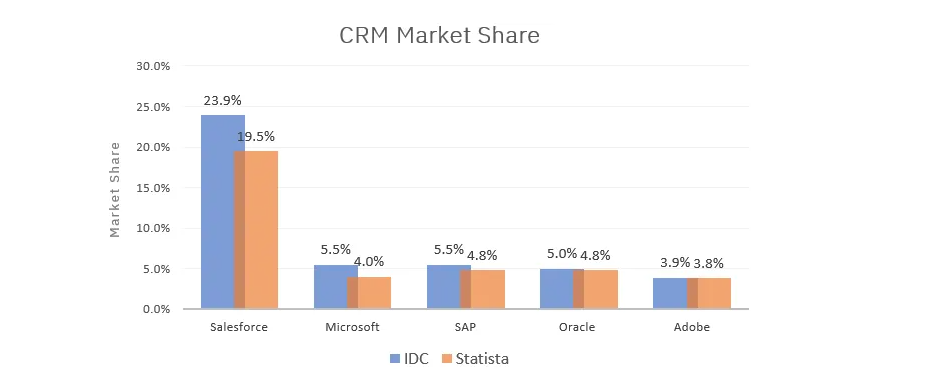
The leading solutions have taken turns in leadership over the years and here are the top Talent CRM market share holders.
- Salesforce: Salesforce commands the worldwide CRM market, boasting a commanding market share of 23.9%, surpassing the collective share of its four closest competitors. More than 60% of the company's revenue comes from existing customers, and the organization is making steady headway in reducing attrition rates.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a suite of business applications that include CRM and enterprise resource planning (ERP) functionality. It's known for seamlessly integrating with Microsoft's other products and services.
- Oracle CX Cloud: Oracle CX Cloud, part of Oracle's broader cloud ecosystem, is a comprehensive CRM solution. It offers tools for sales, marketing, service, and e-commerce.
- SAP Customer Experience (SAP CX): SAP CX is a suite of cloud-based customer experience solutions by SAP. It includes CRM, marketing, e-commerce, sales, and service.
- Adobe Experience Cloud: Adobe Experience Cloud includes Adobe's marketing, advertising, and analytics solutions. It's not a traditional CRM but focuses on improving customer experiences through marketing and data-driven insights.
In 2024, another CRM will enter the chat. LinkedIn announced on October 31st, 2023 its newest feature: LinkedIn CRM Connect.
The latest hiring integration by LinkedIn is set to roll out for customers in early 2024. This integration seamlessly merges LinkedIn Recruiter with candidate relationship management (CRM) systems, providing recruiters with a more straightforward and efficient workflow.
2.3 Talent CRM Businesses' primary revenue stream
The success of CRM platforms hinges upon multiple revenue streams that sustain their business models. Let's dive into some of the key components of a CRM platform's revenue generation:
- Subscription-based SaaS Model: Salesforce, for example, operates on a subscription-based Software as a Service (SaaS) model. Organizations pay a recurring fee for access to Salesforce's CRM platform, including various modules for candidate relationship management.
- Cloud-Based Subscription Model: Workday provides cloud-based HR and financial management solutions, including candidate relationship management. Organizations subscribe to Workday's services and pay on an ongoing basis.
- Subscription-Based Model: Bullhorn typically offers its CRM solutions to staffing and recruiting firms on a subscription basis. Customers pay a regular fee for access to Bullhorn's software, which includes CRM and ATS features.
- Pay-Per-Use or Pay-Per-Hire Models: In some cases, CRM providers catering to high-volume recruitment scenarios, such as staffing agencies, may offer pay-per-use or pay-per-hire pricing models. This allows customers to pay based on the number of candidates processed or hired.
- Customization and Implementation Services: Some CRM solutions offer customization and implementation services as part of their business model. Customers may pay for these services in addition to the subscription fees to tailor the CRM software to their specific needs.
- Freemium or Trial Versions: Some CRM providers offer limited free versions or trial periods of their software to attract potential customers. These may serve as lead-generation tools to convert users into paying subscribers.
3. User Experience with Traditional Talent CRM
Long gone are the days when traditional Talent CRM platforms have been effective in organizing the digital hiring process, yet 37% of Talent CRM platforms are facing limitations when it comes to UX (User Experience).
Traditional CRM systems are used to manage interactions and relationships with customers but with no focus on relationships with candidate management, potential hires, and even past applicants.
Traditional CRM systems don't allow recruiters and hiring teams to manage every stage of the recruitment lifecycle. Meaning, that all the sourcing screening interviewing and onboarding must be done manually.
3.1. Analyzing the Steps in the Recruiter's Journey
The recruiter's experience with Talent CRM platforms is limited since 86% have similar features.
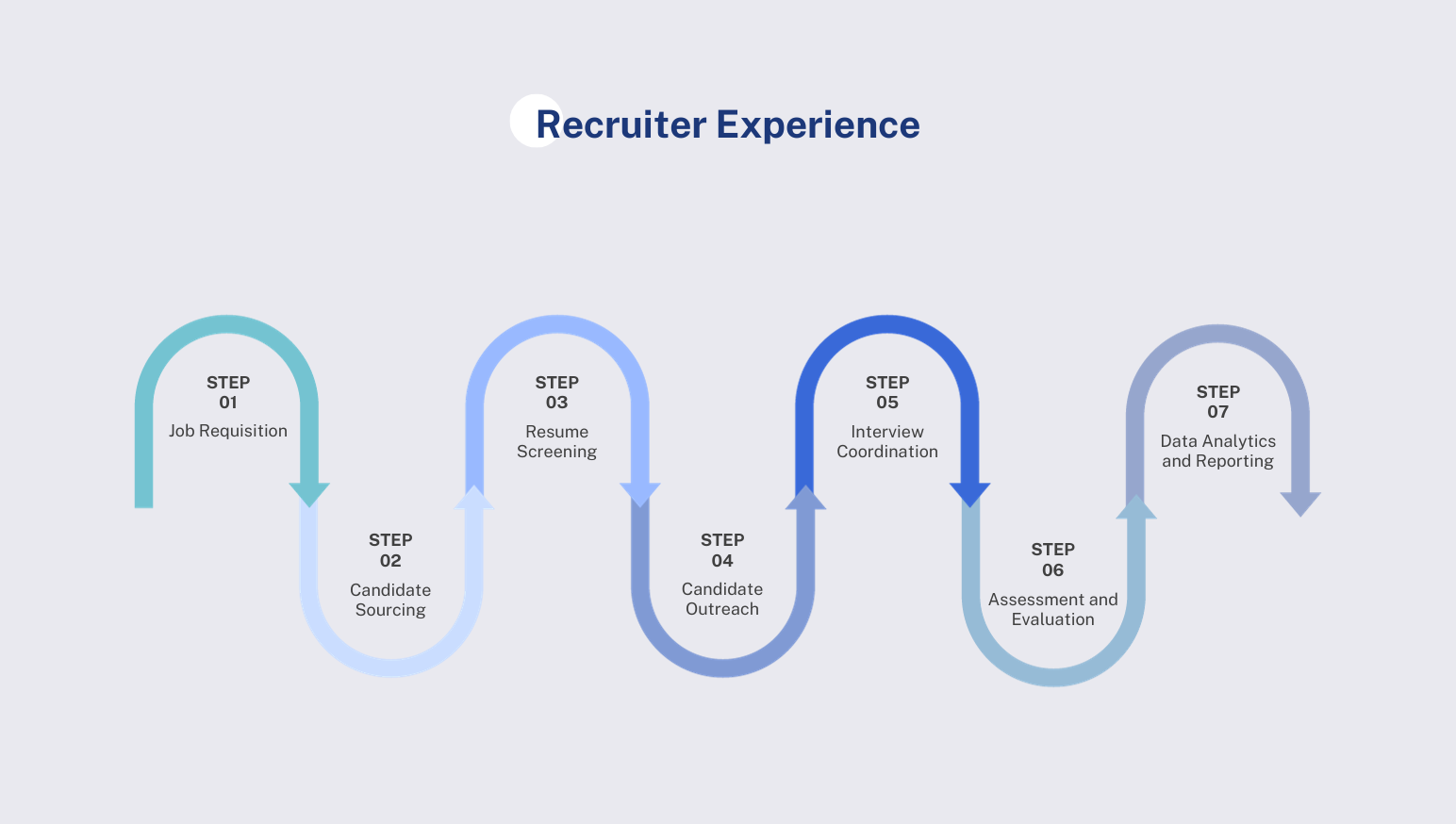
3.1.1 Job Requisition
Strengths:
- Clear identification of staffing needs.
- Efficient communication of job requirements to internal teams.
- Standardized template for requisition creation.
Weaknesses:
- Potential delays in requisition approval processes.
- Inadequate alignment between requisition details and actual hiring needs.
Opportunities:
- Implementing automated approval workflows for faster requisition processing.
- Regular reviews and updates of requisition templates for relevance.
Threats:
- Competing platforms offer faster and more flexible requisition management.
- Inconsistencies in requisition data impacting subsequent stages.
3.1.2 Candidate Sourcing
Strengths:
- Utilization of diverse channels for candidate discovery.
- Integration with external platforms for broader reach.
- Real-time tracking of sourced candidates.
Weaknesses:
- Overemphasis on certain sourcing channels, potentially missing out on untapped talent pools.
- Limited tools for passive candidate engagement.
Opportunities:
- Exploring emerging sourcing platforms and technologies.
- Implementing strategies for building and maintaining a talent pipeline.
Threats:
- Competitors adopting more innovative candidate sourcing techniques.
- Inaccurate sourcing metrics lead to suboptimal decision-making.
3.1.3 Resume Screening
Strengths:
- Automated screening processes for quick candidate shortlisting.
- Customizable screening criteria aligned with job requirements.
- Integration with applicant tracking systems for seamless data transfer.
Weaknesses:
- Potential bias in automated screening algorithms.
- Limited ability to capture nuanced candidate qualifications.
Opportunities:
- Continuous refinement of screening algorithms through machine learning.
- Incorporating user feedback for better algorithmic accuracy.
Threats:
- Negative candidate perception due to a perceived lack of transparency in screening processes.
- Legal challenges related to algorithmic bias.
3.1.4 Candidate Outreach
Strengths:
- Automated communication tools for outreach.
- Personalization options for outreach messages.
- Tracking and analysis of candidate responses.
Weaknesses:
- Risk of candidate disengagement due to excessive or irrelevant outreach.
- Limited integration with social media platforms for outreach.
Opportunities:
- Implementing AI-driven personalization for more effective outreach.
- Expanding outreach channels to include emerging communication platforms.
Threats:
- Competitors offering more sophisticated and personalized candidate outreach.
- Negative impact on employer brand due to poorly executed outreach strategies.
3.1.5 Interview Coordination
Strengths:
- Centralized platform for scheduling and managing interviews.
- Integration with calendar systems for real-time updates.
- Automated reminders and notifications for interview participants.
Weaknesses:
- Potential scheduling conflicts lead to delays.
- Limited support for collaborative scheduling involving multiple stakeholders.
Opportunities:
- Integration with video conferencing tools for virtual interviews.
- Enhanced features for collaborative interview planning.
Threats:
- Competitors are offering more flexible and efficient interview coordination solutions.
- User dissatisfaction due to technical glitches impacting interview scheduling.
3.1.6 Assessment and Evaluation
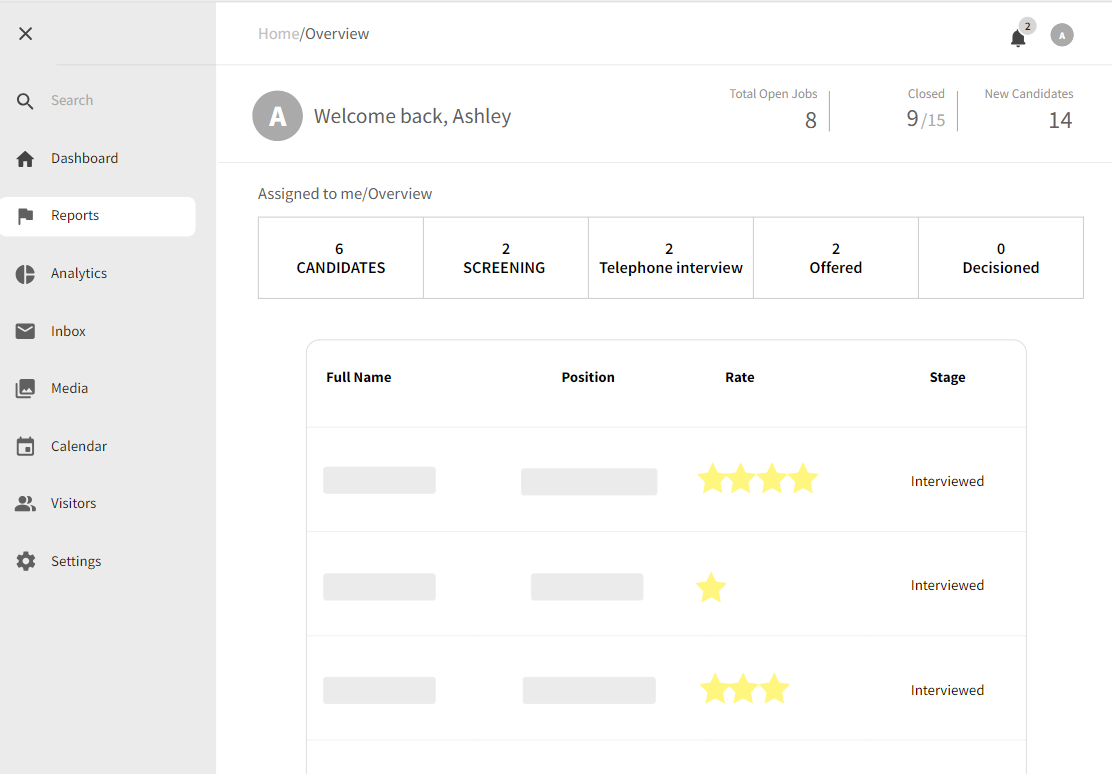
Strengths:
- Standardized assessments for objective candidate evaluation.
- Integration with assessment tools and platforms to match candidates to jobs.
- Transparent communication of assessment results to candidates.
Weaknesses:
- Lack of customization options for assessment criteria.
- Limited support for real-time feedback during assessments.
Opportunities:
- Continuous improvement of assessment methods based on data analytics.
- Incorporating AI for adaptive assessments tailored to individual candidates.
Threats:
- Competitors offer more diverse and comprehensive assessment options.
- Negative candidate experience due to poorly designed or irrelevant assessments.
3.1.7 Data Analytics and Reporting
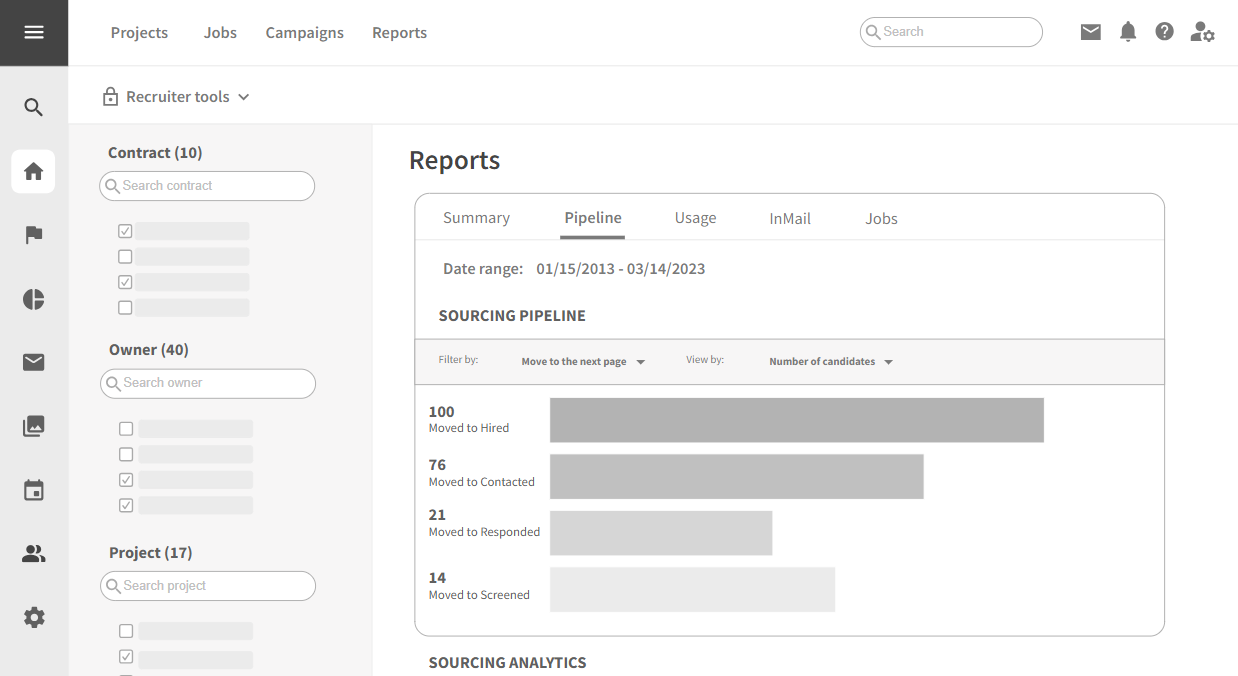
Strengths:
- Comprehensive data analytics for recruitment performance.
- Customizable reports for various stakeholders.
- Real-time dashboards for monitoring key metrics.
Weaknesses:
- Potential information overload with excessive data points.
- Incomplete or inaccurate data impacting decision-making.
Opportunities:
- Implementing predictive analytics for proactive recruitment planning.
- Regular training and upskilling for users to interpret and utilize analytics effectively.
Threats:
- Competitors offering more user-friendly and insightful analytics dashboards.
- Inadequate data security measures lead to concerns about privacy and compliance.
3.2 Analyzing the Steps in the Candidate Journey
3.2.1 Registration
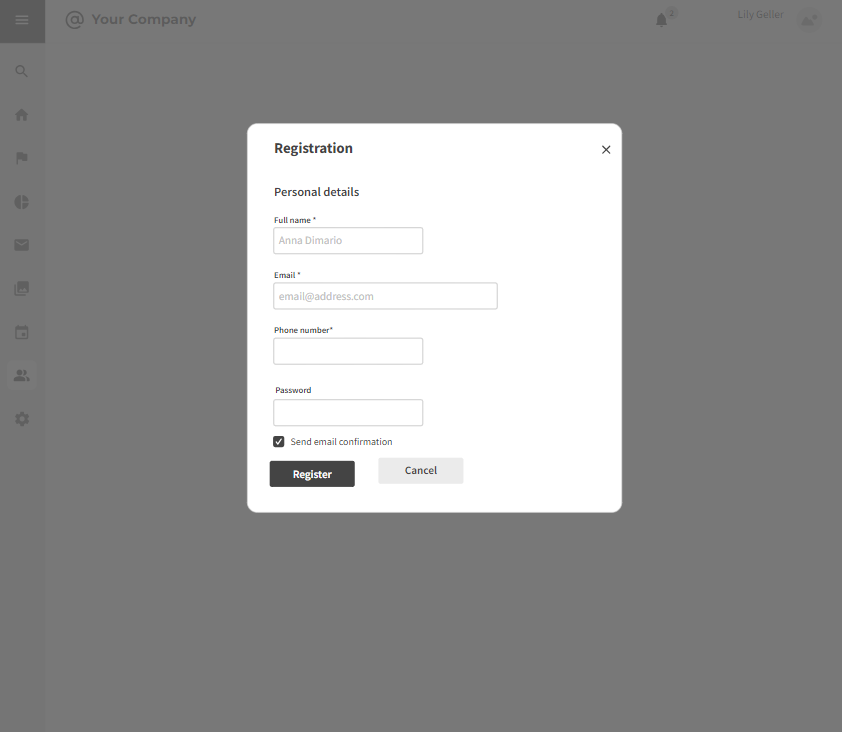
Strengths:
- Streamlined and user-friendly registration process.
- Quick access through various authentication methods (email, social media).
- Clear guidance and tooltips for users.
Weaknesses:
- Potential for user drop-off due to lengthy registration forms.
- Limited options for account recovery in case of login issues.
Opportunities:
- Incorporate multi-step registration to reduce perceived complexity.
- Implement a referral system to boost user acquisition.
Threats:
- Competing platforms with more attractive onboarding experiences.
- Risk of data breaches during the registration process.
3.2.2 Profile Update
Strengths:
- Intuitive and editable user profiles.
- Option for importing data from professional networks.
- Real-time updates for immediate visibility.
Weaknesses:
- Lack of notifications or reminders for incomplete profiles.
- Limited customization options for user profiles.
Opportunities:
- Integration with resume-building tools for a seamless profile update.
- Gamification elements to encourage users to enhance their profiles.
Threats:
- User resistance to sharing comprehensive professional details.
- Inaccurate or outdated information affecting job matching.
3.2.3 Jobs Matching
Strengths:
- Advanced algorithm for accurate job matching.
- Customized job recommendations based on profile data.
- Real-time updates on new job matches.
Weaknesses:
- Over-reliance on algorithms may lead to occasional mismatches.
- Limited transparency on the matching criteria.
Opportunities:
- User feedback mechanism to improve algorithm precision.
- Collaboration with companies to enhance job visibility.
Threats:
- Competitors with more sophisticated job-matching algorithms.
- User frustration from irrelevant job suggestions.
3.2.4 Application Tracking
Strengths:
- Clear and accessible application tracking interface.
- Real-time status updates for applications.
- Notifications for significant status changes.
Weaknesses:
- Limited insights into the decision-making process.
- Lack of personalized feedback on rejected applications.
Opportunities:
- Implement a feedback system for rejected applications.
- Integration with communication tools for direct employer-candidate interaction.
Threats:
- Negative impact on user engagement if application status updates are delayed.
- Competition offering more detailed application tracking features.
3.2.5 Interviewing
Strengths:
- Automated scheduling for interview appointments.
- Integration with calendar applications for seamless coordination.
- Reminders and preparation tips for scheduled interviews.
Weaknesses:
- Potential conflicts with user calendars lead to rescheduling issues.
- Limited support for multi-stage interview processes.
Opportunities:
- Integration with video conferencing tools for virtual interviews.
- AI-driven interview coaching to enhance candidate preparedness.
Threats:
- Competitors offer more flexible and adaptable interview scheduling features.
- Technical glitches affect the reliability of interview formation.
3.2.6 GDPR Update
Strengths:
- Transparent communication on data protection and privacy policies.
- User-friendly interface for managing GDPR preferences.
- Regular updates and compliance checks.
Weaknesses:
- Potential confusion due to complex GDPR language.
- Limited options for users to tailor data-sharing preferences.
Opportunities:
- Educational resources on the platform about GDPR and data security.
- Periodic reminders and updates on privacy features.
Threats:
- Increasing user concerns about data privacy impacting platform trust.
- Regulatory changes require substantial updates to GDPR compliance measures.
4. Building an AI-poweredrequire Talent CRM using HrFlow.ai
New AI-powered Talent CRM systems are revolutionizing how recruiters hire, making it quicker, smarter, and more effective. Companies like HrFlow.ai are leading this transformation with their advanced AI solutions, supercharging the next generation of Talent CRM platforms.
4.1 Enhancing Talent CRM for Recruiters: HrFlow.ai's Key Improvements
Let's check out some of the key improvements HrFlow.ai can bring to the older Talent CRM software:
4.1.1 Job Requisition
- Auto-fill required fields using AI: Recruiters can use HrFlow.ai Tagging API to pre-fill specific job offer fields.
- Enable customizable job posting templates: The Tagging API can adapt to dynamic job templates, offering recruiters more flexibility.
- Refine job descriptions: HrFlow.ai Tagging API can also help you improve your job description SEO by providing relevant keywords and tags.
4.1.2 Candidate Sourcing
- Integrate with more talent pools via API: HrFlow.ai Talent Funnels can help you easily connect to multiple talent pools of candidates.
- Advanced searching and matching with AI: HrFlow.ai Recruiter Copilot offers recruiters advanced searching and scoring capabilities to source candidates efficiently.
- Identify and engage active and passive candidates: HrFlow.ai Searching & Scoring APIs can help you identify and target relevant prospects from various sources.
Read more about Hrflow's latest Scoring algorithm, Cerebro: an advanced AI scoring algorithm.
4.1.3 Resume Screening
- HrFlow.ai's CV parser feature ensures accurate extraction and organization of vital details from resumes in various formats, such as PDF and DOCX.
- HrFlow.ai's resume parsing facilitates better candidate-job matching, by resume and job parsing details and integrating them into your workflow for productivity.
- Also, HrFlow.ai’s Resume Parsing API includes text parsing. how does resume parsing work? By extracting meaningful semantic entities from diverse text inputs. Customize cv/resume parsing settings according to each recruiter’s specific needs, for resume analysis.
4.1.4 Candidate Outreach
- Optimize recruiters' time by exploring automated communication features within HrFlow.ai Workflows.
- Mitigate concerns about platform dependence by using HrFlow.ai Workflows to synchronize data between databases and HrFlow.ai servers. This integration diversifies communication channels, reducing reliance on a single platform.
4.1.5 Interview Coordination
- Set up the various HrFlow.ai Connectors to streamline the process of scheduling interviews with candidates.
- Incorporate HrFlow.ai Workflows ensuring a smooth and engaging experience for both recruiters and candidates in interviews scheduling.
4.1.6 Assessment and Evaluation
- HrFlow.ai's Searching and Scoring APIs can be leveraged for AI-driven search and talent matching, ensuring relevant candidate screening.
- HrFlow.ai's Tagging API allows the assessment of soft skills and cultural fit by analyzing candidates' profiles and experiences.
- HrFlow.ai's Searching and Scoring APIs can efficiently filter out unqualified applications, saving valuable time for recruiters.
4.1.7 Data Analytics and Reporting
- Advanced analytics and customizable reports: HrFlow.ai Usage Reports help recruiters review applicants' volume and sources. Moreover, HrFlow.ai offers structured and comprehensive data about applicants, which helps provide the best insights about your candidates.
4.2 Enhancing Talent CRM for Candidates: HrFlow.aiprofile-building's Key Improvements
4.2.1 Registration
- Implement HrFlow.ai's Job Searching API for rapid and relevant job discovery, reducing the time spent on the sign-up process.
- Leverage HrFlow.ai's Job Searching API and Talent Copilot to optimize the sign-up process for candidates using mobile devices.
- Integrate Text Linking to automate data retrieval, allowing candidates to populate information and streamline the sign-up process effortlessly.
4.2.2 Profile Update
- Utilize Talent Copilot for a seamless and secure profile-building process, overcoming platform limitations and ensuring data privacy.
4.2.3 Match Jobs
- Timely recruiter outreach after applying: HrFlow.ai's Searching and Scoring APIs can facilitate timely recruiter outreach by quickly matching candidates with suitable roles.
- Providing an excellent candidate experience: With HrFlow.ai's Talent Copilot and AI modules, candidates can enjoy a smooth user experience with engaging and positive interactions.
4.2.4 Application Status
- HrFlow.ai's APIs and Workflows can be configured to provide status updates and notifications about application progress.
- HrFlow.ai's connectors can be integrated with the Talent CRM platform tools to track candidates’ applications.
4.2.5 Interview Formation
- Organized interviews scheduled in advance: HrFlow.ai's system can be integrated with scheduling tools to organize interviews in advance.
4.2.6 GDPR Update
- Solutions to simplify GDPR compliance: HrFlow.ai solutions are fully compliant with GDPR regulations. Moreover, HrFlow.aithe recently became the first and only AI solution for processing Talent and Workforce data recognized and cited as a reference by the European Union in its new law on AI risks and personal data protection.
- Automated consent management: The platform can automate consent management, ensuring compliance with GDPR regulations.
- Protect candidate data and privacy: HrFlow.ai is designed with data security and privacy in mind, offering robust measures to protect candidate data.
5. How to Choose the Right Talent CRM for you
Database:
- Prioritize a user-friendly and navigable database.
- Ensure it can handle complex organizational structures.
- Check its capability to manage multiple points of contact within client companies, especially in high-turnover sectors like Construction, Warehousing, Healthcare, and Logistics.
Candidate Workflows:
- Evaluate how the CRM handles candidate workflows.
- Consider if it tracks applications, and assists with onboarding, documentation, contract management, and payroll.
- Check if it integrates with third-party tools for screening and parsing.
Job Posting:
- Assess the job posting capabilities of the CRM.
- Look for comprehensive multi-posting features.
- Consider how well it integrates with third-party multiposters to save time in transferring candidates.
Reporting and Analytics:
- Prioritize CRMs with robust reporting and analytics features.
- Identify reporting criteria relevant to your business goals.
- Acknowledge the importance of proper user training and diligent record maintenance for valuable data analysis.
Pipeline Management:
- Evaluate how the CRM tracks opportunities and provides pipeline management.
- Consider differences in pipeline management between temporary and permanent recruitment.
- Assess how well it supports the three-way sales process involved in recruitment.
Automation and Sequencing:
- Check if the CRM supports communication workflows.
- Ensure it allows automated outreach emails and sequencing for business development.
- Align these features with your marketing outreach, recruitment workflow, and KPI measurement requirements.
Candidate Search:
- Explore candidate searching within the CRM's database.
- Check if it allows external candidate search through multi-poster integrations.
- Leverage reporting features for identifying candidate sources and maximizing the return on investment.
Additional Considerations:
- Account for factors like recruitment specialization, system deployment (cloud-based or local), third-party integrations, customization options, the importance of AI or automation, scalability, and vendor support structure.
6.Conclusion and Key Takeaways
As the AI revolution continues to reshape the recruitment landscape, AI-powered CRM solutions have empowered recruiters with unprecedented capabilities, demanding a recalibration of traditional approaches.
This case study has illuminated the genesis of these platforms and their impact on both recruiters and job seekers within the evolving white-collar job market.
Looking ahead, the future of talent CRM appears promising yet challenging. Innovations in AI will likely further augment the efficiency and personalization of recruitment processes. However, this progression will necessitate continuous adaptation and learning. Recruiters will need to navigate ethical considerations and balance the efficiency of AI with the human touch necessary for meaningful candidate engagement.
The evolution of talent CRM is an ongoing narrative, one where the fusion of technological advancements and human insight will shape the recruitment landscape. Embracing this future with adaptability and a keen eye on ethical and human-centric practices will be the cornerstone of success in this continually evolving domain.

