Summary
In this article, we'll look closely at the evolving landscape of Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) in modern recruitment as the war for top talent continues to heat up.
Our focus will be on the transformative impact of AI-powered ATS software, highlighting their ability to offer deeper candidate insights, automate workflows, and create more streamlined experiences for recruiters and candidates alike.
- The article delves into the history and market landscape of ATS software
- It examines the current limitations of traditional ATS solutions and their impact on candidate and recruiter experience.
- It also focuses on the transformative potential of AI-powered ATS platforms in revolutionizing hiring processes for organizations.
Table of contents
- Overview
1.1. Abstract - History and Market Landscape of ATS
2.1. Key drivers of the expanding ATS market
2.2 Top leading ATS solutions in the 2024 market
2.3 ATS Businesses' Primary Revenue Stream - User Experience with Traditional ATS
3.1. Analyzing the Recruiter's Experience
3.2. Analyzing the Candidate's Experience - Building an AI-powered ATS using HrFlow.ai
4.1. Enhancing Recruiter's Experience with HrFlow.ai
4.2. Enhancing Candidate's Experience with HrFlow.ai - How to choose the right ATS for you
- Conclusion and Key Takeaways
1. Overview
1. 1. Abstract
The war for talent is fiercer than ever in today's competitive hiring landscape. Organizations are looking to streamline their recruiting and hiring processes to source, attract, and retain top talent more effectively. This has driven the rapid adoption of applicant tracking systems (ATS) over the past decade.
ATS software aims to automate and simplify the hiring process for both recruiters and candidates. By centralizing and organizing candidate applications and profiles, ATS systems allow recruiters to post jobs, screen resumes, and manage the hiring workflow. This enables recruiting teams to handle high application volumes and reduce manual hiring tasks.
However, many organizations are finding that traditional ATS solutions have limitations when it comes to providing insights about applicants or optimizing the experience. Recruiters still spend significant time on pre-screening candidates, while job seekers feel disconnected from the black-box application process.
This is where artificial intelligence (AI) comes in. The next generation of Applicant Tracking Systems is leveraging AI to transform the user experience for recruiters and candidates and enable deeper candidate insights, automated workflows, and more streamlined experience. As AI capabilities continue advancing, ATS solutions will become even smarter at matching the right candidates to the right roles.
This article explores the evolution of applicant tracking systems and how the integration of AI is reshaping modern recruiting. We'll examine the key benefits of AI-powered ATS software for both recruiters and candidates and how they aim to make hiring smarter, faster, and more effective.
2. History and Market Landscape of ATS
Applicant tracking systems emerged in the 1990s as companies sought ways to manage the influx of applications and transition away from paper-based hiring. Early ATS platforms focused mainly on providing databases to parse, organize, and store resumes, job postings, and applicant profiles digitally.
As online recruiting grew in the 2000s, so did the adoption of applicant-tracking technology. HR teams needed ways to easily post openings on multiple job boards, receive resumes electronically, parse resumes into a neatly organized excel tables, and screen candidates at high volumes.
2.1 Key drivers of the expanding ATS market
Key drivers of the expanding ATS market included:
- Accelerating the war for talent with the need to hire quickly
- Shift to digital resumes and online job distribution
- Desire to reduce recruitment costs and eliminate paper processes
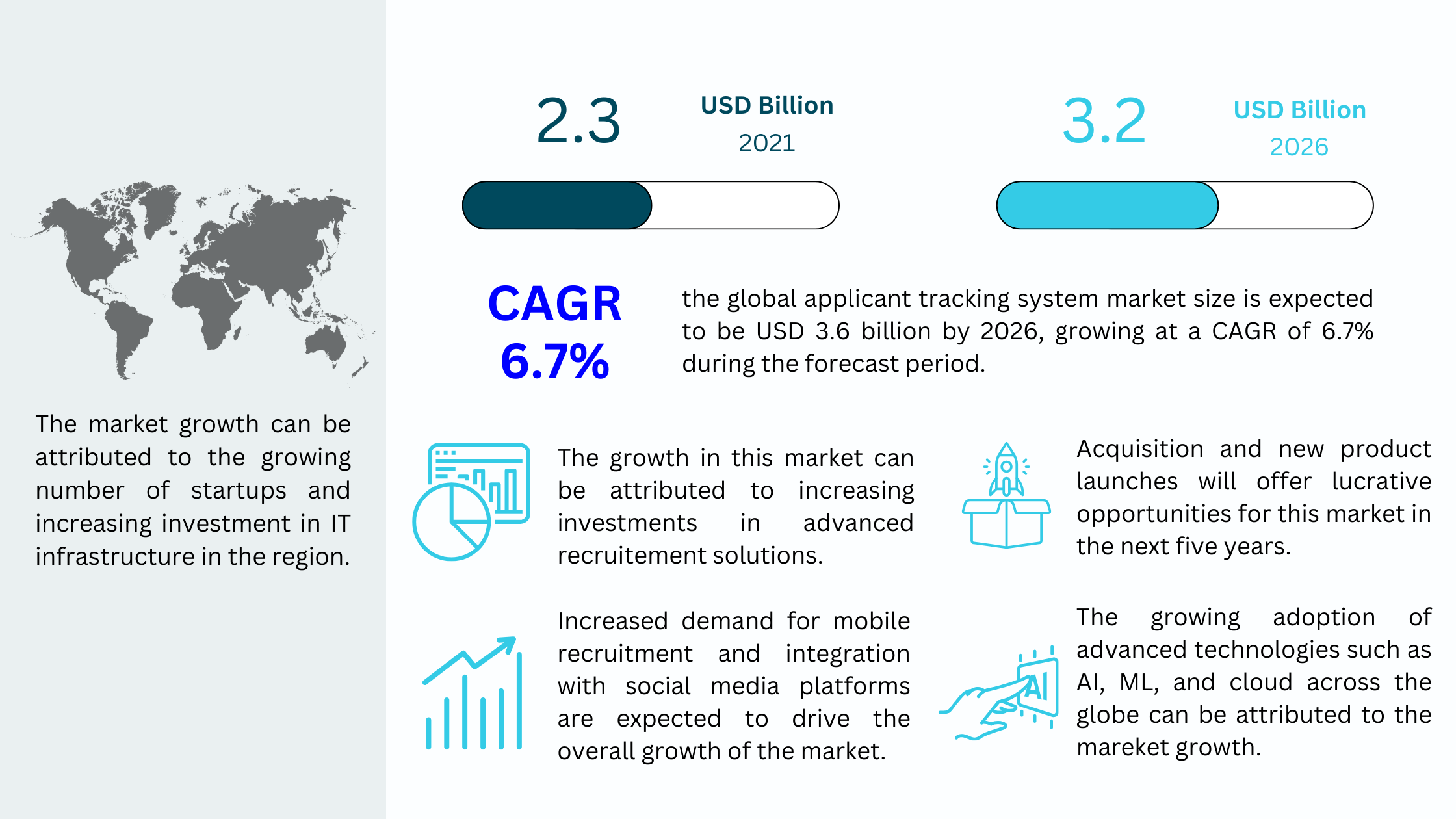
According to research firm Grand View Research, the global ATS market surpassed $2.3 billion in 2021 and is poised to grow at a CAGR of 6.7%, with expectations of surpassing $3.2 billion by the conclusion of 2026.
This growth reflects the mission-critical role ATS platforms now play in hiring.
2.2 Top leading ATS solutions in the 2024 market
- SAP SuccessFactors: Comprehensive human capital management solution encompassing recruitment, performance, and learning. Aligns HR strategies with business goals for optimized workforce management.
- Workable: User-friendly recruiting software streamlining hiring with applicant tracking, collaboration, and interview scheduling for efficient candidate evaluation and selection.
- Bullhorn: The solution made for staffing and recruiting agencies, streamlining candidate sourcing, tracking, and placement, as well as client management.
- Lever: The ATS focuses on sourcing, tracking, and managing candidates while emphasizing team collaboration and data-driven insights.
- Zoho Recruit: Cloud-based ATS with customizable workflows, aiding efficient candidate sourcing, assessment, and engagement throughout the hiring process.
- Greenhouse: Structured recruiting platform with job posting, candidate evaluation, interview scheduling, and analytics tools for targeted talent acquisition.
- SmartRecruiters: End-to-end talent acquisition suite enabling collaboration and data-driven hiring. Combines marketing, tracking, and reporting to attract top talent.
- Oracle Taleo: Offers HR solutions, including talent acquisition, management, and development, aiding employee sourcing, onboarding, and retention.
- iCIMS: Recruitment software platform focusing on applicant tracking and automation—Simplifies sourcing, assessment, and communication for streamlined hiring.

As talent competition continues to rise, organizations are demanding more advanced recruiting capabilities from ATS solutions. This is fueling innovation around AI-powered systems that go beyond basic application tracking.
2.3 The ATS Business Model
The primary revenue stream for the ATS business comes from subscription fees. Here's a breakdown of the essential elements of this business model:
- Subscription-Based Plans: Most ATS systems offer tiered subscription plans, providing customers with different levels of access to the platform's features based on the number of recruiters or users they need. One example is Greenhouse, which offers different pricing tiers based on the number of users and features required.
- Freemium: Some ATS providers offer a freemium model, granting access to basic features at no cost while offering premium features, customization, or additional services at a fee. Workable provides a freemium option that includes basic features, allowing businesses to start recruiting without immediate financial commitment.
- Add-Ons and Upselling: The solutions offer add-on features and premium services that customers can purchase to enhance their ATS experience, such as advanced reporting and integration with other HR tools. Brands like Zoho Recruit offer premium services like advanced analytics and custom integration options.
- Enterprise Solutions: The software provides customized enterprise solutions with specialized features and support for large organizations with complex requirements. ATS providers like Oracle offer customized enterprise solutions tailored to the specific needs of large organizations.
- Pay-as-You-Go: This model provides flexibility by charging businesses based on their actual usage; it’s useful for organizations with fluctuating hiring needs, allowing them to adapt their spending in alignment with their recruitment activity. SmartRecruiters offers a pay-as-you-go model, providing flexibility and cost control.
3. User Experience with Traditional ATS
While traditional ATS platforms helped organize the hiring process digitally, many still face limitations when it comes to user experience. Recruiters, candidates, and employees all face friction with legacy applicant tracking systems.
3.1. Recruiter Experience with traditional ATS
The recruiter's journey and the Applicant Tracking System (ATS) are closely intertwined throughout the hiring process. ATS is the primary tool recruiters and HR professionals use to manage and streamline recruitment efforts.
3.1.1 Analyzing the Recruiter's Experience
Here are some main steps in the recruiter's experience to find their next hires:
3.1.1.1 Job Creation
Strengths:
- Allows recruiters to define job requirements and postings.
- Collaborative input from recruiters and hiring managers.
Weaknesses:
- Time-consuming and often manual process.
- Inflexible job templates that may not cater to all roles.
- Difficulty capturing nuances.
Threats:
- Risk of failing to attract the right talent due to inadequate job descriptions.
- Unclear requirements lead to unqualified applicants.
Opportunities:
- Leverage AI to fill required fields automatically and create customizable posting creation.
- Use of data analytics to refine job requirements and descriptions.
3.1.1.2 Job Posting
Strengths:
- Ability to post to multiple job board platforms.
- Potential for broad audience reach.
Weaknesses:
- Repetitive and often manual posting processes.
- Limited integration with social media and networks.
- No optimization of job advertisements.
Threats:
- Smaller applicant pool due to limited reach.
- Rapidly changing job board algorithms that may affect visibility.
Opportunities:
- Automated AI-powered job distribution.
- Integration with more platforms like social media.
- Optimization of job posts for maximum visibility.
3.1.1.3 Talent Sourcing
Strengths:
- Using multiple channels for sourcing candidates
- Building a pipeline of prospects
Weaknesses:
- Inadequate search capabilities
- Flawed matching algorithms
- Lack of integration with talent pools
- Minimal passive candidate engagement
- No leveraging of emerging channels
Threats:
- Failure to identify and engage with qualified candidates
Opportunities:
- Advanced search and matching capabilities
- Integration with more talent pools and channels
- Tools to identify and engage passive candidates
- Leverage emerging channels through API integration
3.1.1.4 Talent Pool
Strengths:
- Centralized database of candidate profiles
- Ability to filter and search talent pool
- A single place to source active and passive candidates
Weaknesses:
- No automatic profile enrichment
- Minimal re-engagement capabilities
- Outdated candidate profiles
- Fragmented view from various sources
Threats:
- Unreliable and incomplete data on candidates
- Losing touch with prospects
Opportunities:
- Automated profile enrichment from other sources
- Ongoing nurturing of prospects
- Unified profile view assimilating data from various sources
3.1.1.5 Candidate Assessment
Strengths:
- Keyword search to filter candidates
- Resume parsing algorithm and matching algorithms, though basic
- Technical and personality tests
Weaknesses:
- Limited search capabilities
- Simplistic or biased matching algorithms
- Irrelevant applications
- No evaluation of soft skills and culture fit
Threats:
- Qualified candidates getting screened out
- Time wasted on unqualified candidates
Opportunities:
- Advanced semantic search capabilities with resume parsing tools
- Relevant, nuanced, and unbiased matching algorithms
- Automated screening tools assessing soft skills and culture fit
3.1.1.6 Candidate Activation
Strengths:
- Review and re-activate past applicants
- Maximizes the value of the existing candidate database.
- Saves time by re-engaging past applicants.
Weaknesses:
- Difficulty identifying relevant past prospects
- Outdated contact data
- Ineffective outreach strategies for past candidates.
Threats:
- Unable to tap into previously interested candidates
- Market dynamics may change, making past candidates less relevant.
Opportunities:
- Intelligent re-targeting of prospects based on fit
- Enriching contact data from other sources with resume parser API
- Integration with email and communication platforms
3.1.1.7 Reports and Insights
Strengths:
- Basic reporting on application volume and sources
- Helps identify successful sourcing channels.
Weaknesses:
- Lack of advanced and customizable reporting
- Insufficient depth in data analysis for strategic decision-making.
- No predictive analytics
Threats:
- Inability to make data-driven recruitment decisions
Opportunities:
- Advanced analytics and customizable reports
- Provide actionable insights into process and performance
- Predictive analytics to forecast hiring needs and targets
3.2. Candidate Experience with traditional ATS
The candidate journey encompasses all interactions and touchpoints that job seekers have with a company during the hiring process. Providing an excellent candidate experience is crucial for attracting top talent in a competitive market.
3.2.1 Analyzing the Steps in the Candidate's Experience
Here are the main steps in the candidate's experience when exploring new job opportunities.
3.2.1.1 Sign up
Strengths:
- Efficient Data Collection: Enables comprehensive gathering of candidate data.
- Standardized Process: Ensures consistency in capturing essential details.
- Seamless Workflow Integration: Integrates smoothly into overall recruitment processes.
Weaknesses:
- Lengthy Process: Potential for candidate frustration and drop-offs.
- Suboptimal User Experience: Limited user-friendly design may deter applicants.
- Redundant Data Entry: Repetitive data input for candidates.
Opportunities:
- Automation Integration: Streamline the process with an automated data population.
- Enhanced Customization: Tailor the 'Sign Up' step to specific organizational needs.
Threats:
- Candidate Drop-off: Lengthy processes may lead to applicant abandonment.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Outdated systems may disadvantage organizations.
- Security Concerns: Risk of data exposure without robust security measures.
3.2.1.2 Job Search
Strengths:
- Ability to access numerous job offers from job boards, career sites, etc.
- Using filters to select the most relevant job offers.
Weaknesses:
- Fragmented job search across multiple sites.
- Lack of personalization in search results.
- Difficulty finding the right openings.
Threats:
- Irrelevant jobs overwhelming job seekers.
- Discouraging experience leads candidates to give up.
Opportunities:
- Intelligent job recommendations based on experience and interests.
- Enhanced search and discovery through AI.
3.2.1.3 Job Application
Strengths:
- Quick-apply features on some sites.
- Ability to upload a resume.
Weaknesses:
- Time-consuming job applications.
- Repetitive form filling.
- No tracking of application status.
Threats:
- Tedious applications deter candidates from applying.
- Technical issues or lack of mobile experience.
- Applications getting lost or ignored.
Opportunities:
- Simplified application experience through integrations.
- Auto-fill of application fields.
- Status tracking and notifications.
3.2.1.4 Job Matching
Strengths:
- Initial screening call or chat.
- Early interaction with the recruiter.
Weaknesses:
- Delayed or no response after applying.
- Minimal insight into role or culture.
Threats:
- No follow-up from recruiters discourages candidates.
- Negative interactions reflect poorly on the employer brand.
Opportunities:
- Timely outreach and scheduling by recruiters.
- Recruiters prepared with role details.
- Providing a good candidate experience.
3.2.1.5 Interview Process
Strengths:
- Direct interaction with the hiring team.
- Chance to demonstrate abilities.
Weaknesses:
- Unclear or last-minute scheduling.
- Repeating introductions and questions.
- Minimal feedback.
Threats:
- Disorganized experience frustrates candidates.
- Limited transparency or feedback loses candidates.
Opportunities:
- Organized interviews coordinated in advance.
- Structured process and communication.
- Actionable interview feedback.
3.2.1.6 Job Alerts
Strengths:
- Notifications for relevant job postings.
- Engagement of passive candidates.
Weaknesses:
- Irrelevant alerts and noise.
- Alert fatigue leading to opt-outs.
Threats:
- Excessive alerts considered spam.
- Data shared without explicit consent.
Opportunities:
- Intelligent matching for useful alerts.
- Appropriate alert frequency and channel preferences.
- Keeping passive candidates engaged.
3.2.1.7 GDPR Compliance
Strengths:
- Protection of candidate data and privacy.
- Increased transparency.
Weaknesses:
- Complex regulations to interpret.
- Administrative overhead for compliance.
Threats:
- Private candidate data being collected without consent.
- Fines and lawsuits for non-compliance.
- Loss of candidate trust.
Opportunities:
- Solutions to simplify GDPR compliance.
- Automated consent management.
4. Building an AI-Powered ATS using HrFlow.ai
Emerging AI capabilities transform traditional ATS platforms and allow organizations to make hiring smarter, faster and more effective.
HrFlow.ai has become a leader in this space by using cutting-edge AI solutions to supercharge the next generation of Applicant Tracking Systems with amazing capabilities. Here are some of the primary improvements HrFlow.ai can make to legacy ATS software:
4.1. AI-powered ATS for Recruiters
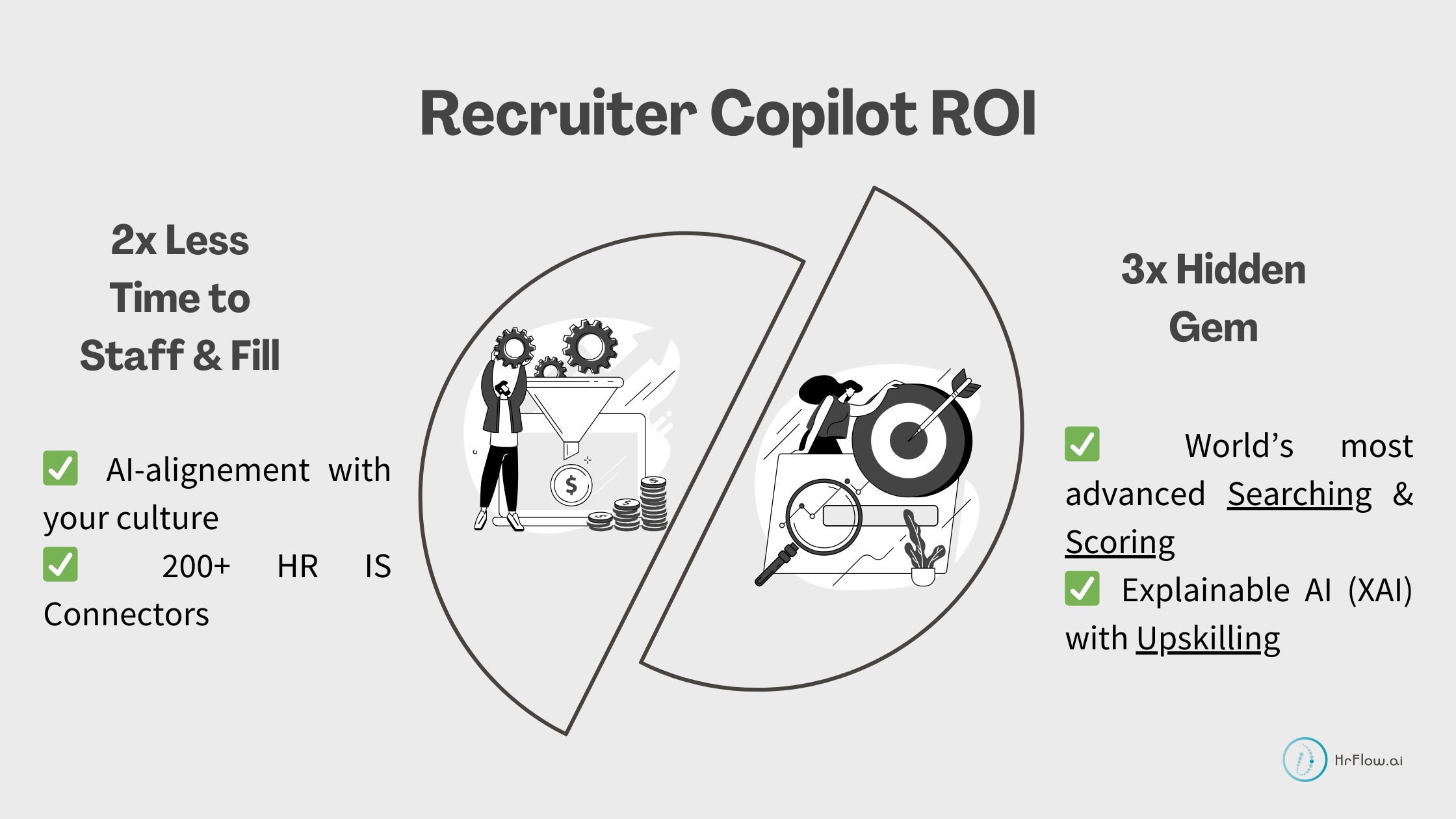
4.1.1. Job Creation
- Auto-fill required fields using AI: Recruiters can use HrFlow.ai Tagging API to pre-fill specific job offer fields.
- Enable customizable job posting templates: The Tagging API can adapt to dynamic job templates, offering recruiters more flexibility.
- Refine job descriptions: HrFlow.ai Tagging API can also help you improve your job description SEO by providing relevant keywords and tags.
4.1.2. Job Posting
- Automated job posting to relevant channels: HrFlow.ai Talent Funnels allows Recruiters to post their job offers to multiple channels thanks to its impressive library of 200+ connectors.
- HrFlow.ai can also help create custom workflows that follow specific business logic set up by the client.
4.1.3. Candidate Sourcing
- Integrate with more talent pools via API: HrFlow.ai Talent Funnels can help you easily connect to multiple talent pools of candidates.
- Advanced searching and matching with AI: HrFlow.ai Recruiter Copilot offers recruiters advanced searching and scoring capabilities to source candidates efficiently.
- Identify and engage active and passive candidates: HrFlow.ai Searching & Scoring APIs can help you identify and target relevant prospects from various sources.
Read more about HrFlow.ai's pre-trained model of Scoring algorithm, Cerebro: an advanced AI scoring algorithm.
4.1.4. Talent Pool
- Auto-enrich candidate profiles using various data sources: HrFlow.ai Resume Parsing and Tagging APIs can automatically enrich candidate profiles by CV parsing and organizing data from various data sources.
- Nurture prospects through ongoing engagement: Use HrFow.ai to set up customized newsletters for candidates, presenting the latest and most relevant job offers to them.
- Unified and up-to-date profile view: HrFlow.ai's Storing API ensures a unified and constantly updated view of candidate profiles from various sources.
Read more about the importance of structuring data to HR software companies with resume parsing soft, here.
4.1.5. Candidate Assessment
- Relevant screening with AI searching and Matching: HrFlow.ai's Searching and Scoring APIs can be leveraged for AI-powered search and matching, ensuring relevant candidate screening. These APIs seamlessly integrate with your current ATS.
- Assess soft skills and cultural fit: HrFlow.ai's Tagging API allows the assessment of soft skills and cultural fit by analyzing candidates' profiles and experiences.
- Save time and reduce unqualified applications: HrFlow.ai's Searching and Scoring APIs can efficiently filter out unqualified applications, saving valuable time for recruiters.
4.1.6. Candidate Activation
- Intelligent retargeting of past prospects: HrFlow.ai Searching & Scoring APIs can help you identify and re-target relevant prospects from the past that could fit your current job openings.
- Auto-enrich contact data: for CV parsing, HrFlow's AI-powered Resume Parsing API, Text Parsing, and Tagging APIs can automatically update and enrich candidate contact data, regardless of the batch of resumes' volume.
- Integrate with communication platforms: HrFlow.ai's various connectors allow integration with communication platforms for streamlined candidate engagement.
4.1.7. Reports and Insights
- Advanced analytics and customizable reports: HrFlow.ai Usage Reports help recruiters review applicants' volume and sources. Moreover, HrFlow.ai offers structured and comprehensive data about applicants, which helps provide the best insights about your candidates.
4.2. AI-powered ATS for Candidates
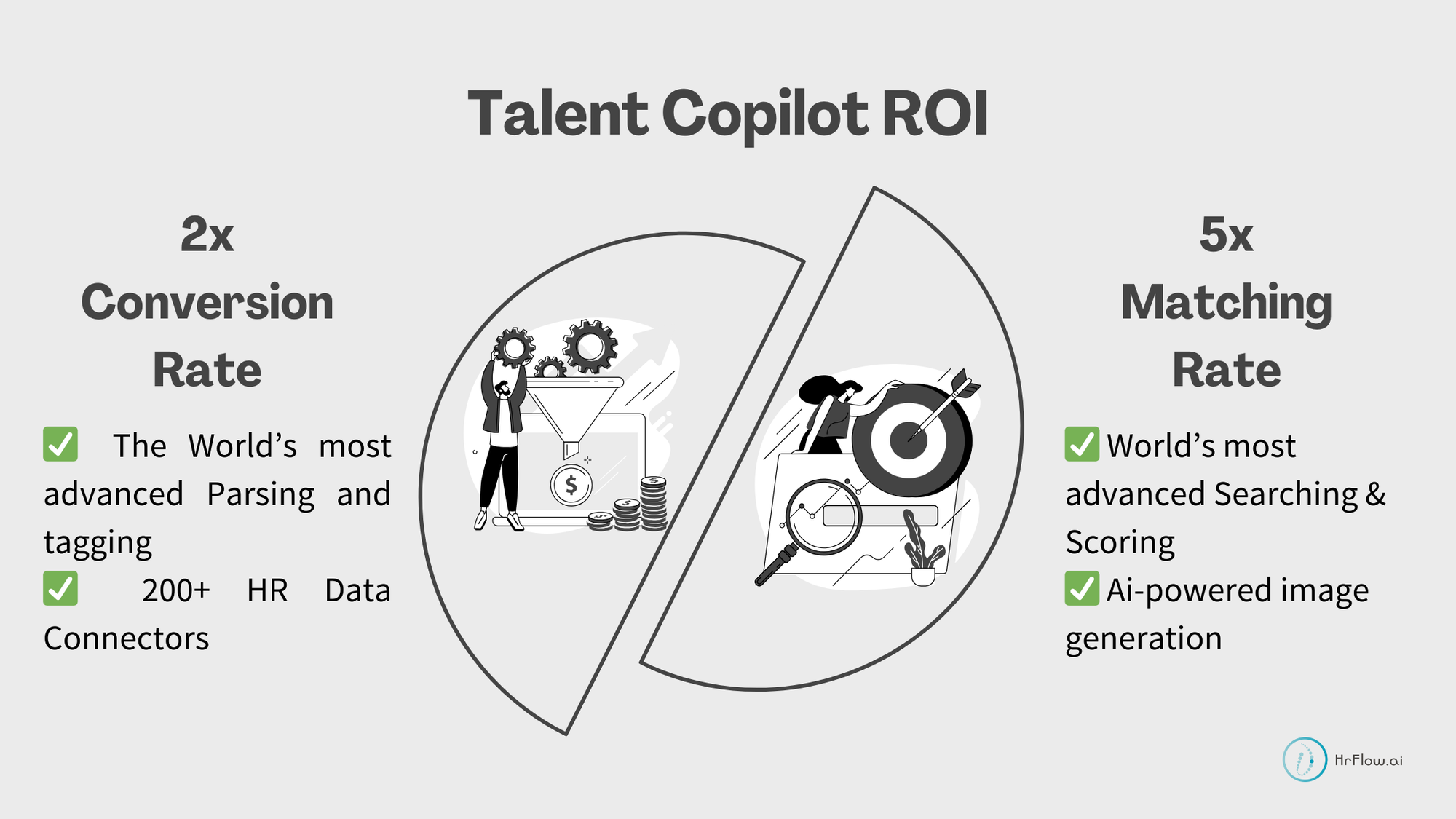
4.2.1. Sign Up
- Implement HrFlow.ai's Job Searching API for rapid and relevant job discovery, reducing the time spent on the sign-up process.
- Leverage HrFlow.ai's Job Searching API and Talent Copilot to optimize the sign-up process for candidates using mobile devices.
- Integrate Text Linking to automate data retrieval, allowing candidates to effortlessly populate data and streamline the sign-up process.
4.2.2. Job Search
- Intelligent job recommendations using AI: The HrFlow.ai Talent Copilot can provide intelligent job recommendations tailored to candidates' profiles, resumes, and preferences.
- Enhanced search based on experience and interests: HrFlow.ai's Searching API, integrated with the Rating and Tracking APIs, can offer an enhanced search experience based on a candidate's interests and experience.
4.2.3. Job Application
- Auto-fill application fields using AI: HrFlow.ai's AI-powered Resume Parsing and Tagging APIs can automatically fill in application fields, reducing manual entry for candidates.
- Simplified applications through integrations: HrFlow.ai's various connectors enable a simplified job application process through seamless integrations with 200+ connectors.
- Status tracking and notifications: HrFlow.ai's Tracking API and Workflows can be configured to provide status updates and notifications about application progress.
4.2.4. Job Matching
- Timely recruiter outreach after applying: HrFlow.ai's Searching and Scoring APIs provide candidate matching insights.
- Providing an excellent candidate experience: With HrFlow.ai's Talent Copilot and resume analysis APIs, candidates can enjoy a smooth user experience with engaging and positive interactions.
Read more about HrFlow's human-level job-talent matching algorithms. here.
4.2.5. Interview Process
- Organized interviews scheduled in advance: HrFlow.ai's system can be integrated with scheduling tools to organize interviews in advance.
4.2.6. Job Alerts
- Intelligent matching for relevant alerts: HrFlow.ai leverages its AI-powered Scoring algorithms to help send intelligent and customized job alerts.
4.2.7. GDPR Compliance
- Solutions to simplify GDPR compliance: HrFlow.ai solutions are fully compliant with GDPR regulations. Moreover, HrFlow.ai recently became the first and only AI solution for processing Talent and Workforce data recognized and cited as a reference by the European Union in its new law on AI risks and personal data protection.
- Automated consent management: The platform can automate consent management, ensuring compliance with GDPR regulations.
- Protect candidate data and privacy: HrFlow.ai is designed with data security and privacy in mind, offering robust measures to protect candidate data.
5. How to choose the right ATS for you
When exploring an Applicant Tracking System (ATS), understanding what ATS features to look for and the right questions to ask is paramount.
Delve into the evaluation process by considering these essential aspects:
5.1 What to Look for in an ATS
In your quest for an ATS, it's crucial to scrutinize its features and functionalities. Consider aspects such as scalability, ATS resume parser, user experience, analytics capabilities, and industry relevance.
Evaluate if the ATS aligns seamlessly with your unique recruitment needs, offering features that address specific challenges.
5.2 Questions to Ask About an Applicant Tracking System
- Functionality Fit: How well does the ATS align with the specific needs of our recruitment process, and does it offer features to address our unique challenges?
- Scalability: Can the ATS adapt to our evolving business size and recruitment demands, ensuring seamless integration as we grow?
- User Experience: Is the ATS intuitive and user-friendly for both recruiters and candidates? How does it enhance the overall candidate experience?
- Analytics Capabilities: Does the ATS provide robust analytics from submitted resumes. And how can these insights help us optimize our recruitment strategies and processes?
- Cost and ROI: What is the cost structure, and how does it fit into our overall recruitment budget? Can the ATS demonstrate a positive return on investment?
- Industry Relevance: Does the ATS have features tailored to our industry, addressing specific challenges and enhancing our recruitment efficiency?
- Integration Possibilities: How well does the ATS integrate with our existing tools and systems, fostering a seamless workflow within our recruitment ecosystem?
- Mobile Accessibility: Is the ATS optimized for mobile use, considering that a significant percentage of candidates use mobile devices for job searches?
- Support and Training: What support mechanisms does the ATS provider offer? Are there training sessions during onboarding, comprehensive documentation, and ongoing customer support?
- Customization Options: Does the ATS allow for customization, such as tailored workflows and reports, to meet our unique recruitment processes and reporting needs?
5.3 ATS Integrations
Additionally, consider the integration capabilities of the ATS, like the ATS resume parser, ensuring it harmonizes with your existing workflows and tools. The ability to seamlessly integrate with other tools enhances the overall efficiency of your recruitment ecosystem.
By combining a focus on what to look for in an ATS and the right questions to ask, you'll embark on a comprehensive assessment, ultimately selecting an ATS that meets your organization's specific needs.
6. Conclusion and Key Takeaways
The journey through the evolution of Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) reveals a significant shift from traditional methods to AI-powered solutions.
This transformation reflects an overarching theme in the recruitment industry: the need for efficiency, effectiveness, and a more human-centric approach.
The integration of AI in ATS is not just a technological upgrade; it's a paradigm shift in how we approach talent acquisition.
As we move forward, it's crucial to balance technological advancements with human insight, ensuring that recruitment remains a people-centric process, aided, but not overshadowed, by technology.
The promise of AI in recruitment is vast, and its continuous evolution will undoubtedly shape the future of work and talent acquisition in unprecedented ways.
